Scientists placed healthy adults in an MRI scanner. They measured brain volume. They tested memory and mental speed. Then they asked a simple question: What happens if people take omega-3 supplements consistently?
Brain scans showed changes that typically take months to appear. Memory scores climbed. Mental fog lifted. And the benefits kept growing week after week.
This isn’t just another vitamin fad. Your brain needs omega-3 fatty acids to function. Without them, it can’t build new cells. It can’t send signals properly. It can’t maintain its structure.
Let’s look at what happened during those weeks of supplementation — and why it matters for your brain.
The “fatty” brain: why omega-3s are essential
Your brain on fats
Your brain is 60% fat. That’s not a problem. It’s by design.
Every cell in your brain sits wrapped in a fatty membrane. This coating decides what gets in and what stays out. It controls how fast signals travel. It affects how well you think.
But not all fats are equal. Your brain craves specific types. Omega-3 fatty acids top that list.
Meet the players: DHA, EPA, and ALA
Three main omega-3s affect your brain:
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) makes up 97% of the omega-3 fats in your brain. It builds cell membranes. It helps neurons grow. It keeps your brain flexible and responsive.
EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) fights swelling in brain tissue. It regulates mood. It protects neurons from damage.
ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) comes from plant sources. Your body converts small amounts into DHA and EPA. But the process is slow and inefficient — only about 5-10% gets converted.
Think of DHA as the builder, EPA as the protector, and ALA as the backup plan.
The omega-6 problem
Most people eat too little omega-3. But there’s more to the story.
Modern diets contain far too much omega-6 fatty acid. These fats come from vegetable oils, processed foods, and grain-fed meat. While you need some omega-6, the balance matters.
The ideal ratio sits around 1:4 or even 1:2 (omega-3 to omega-6). The average American eats a ratio closer to 1:16. Some people hit 1:20.
Why does this matter? Omega-6 and omega-3 compete for the same space in your cells. When omega-6 floods your system, omega-3 can’t get in. Your brain starves even if you take supplements.
Common omega-6 sources to limit:
- Soybean oil
- Corn oil
- Sunflower oil
- Most fried foods
- Packaged snacks
Switching to olive oil and eating more fish creates a better balance. Your brain will thank you.
Signs you might need more omega-3s
Check yourself against these common symptoms:
- Dry, flaky skin or brittle nails
- Constant fatigue or poor sleep quality
- Trouble focusing or brain fog
- Joint pain or stiffness
- Mood swings or feeling down
- Memory problems or mental slowness
- You eat fish less than once a week
Three or more? Your omega-3 levels might be low.
The timeline: what really happened
Week 2: the fog begins to lift
Participants noticed changes fast. Mental clarity improved. Focus sharpened. Tasks that felt draining became easier.
One woman described it like this: “It’s like someone turned up the brightness on my thoughts.”
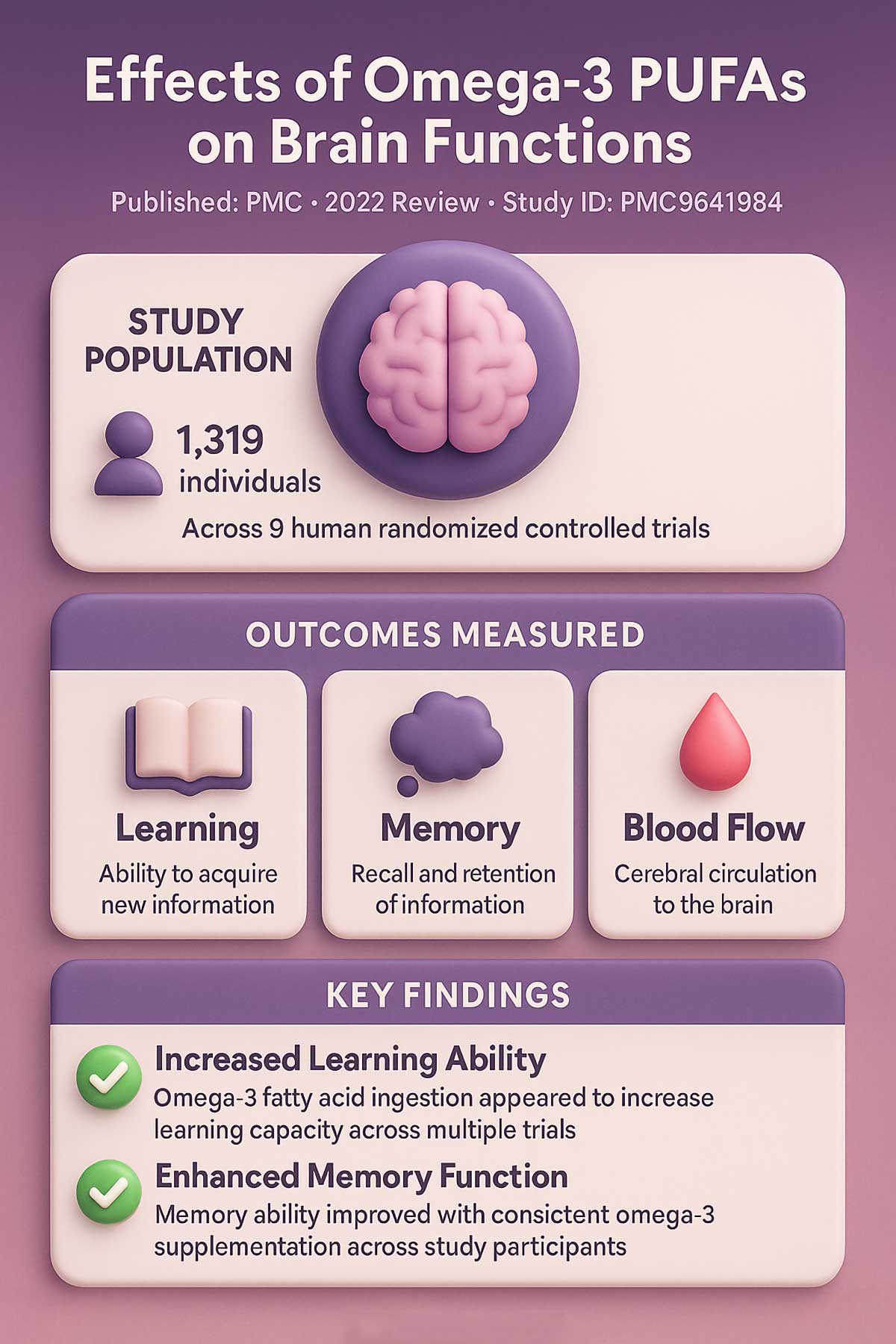
A 2022 review looked at nine studies with 1,319 people. Researchers found that omega-3 intake seemed to boost learning and memory ability within weeks. Blood flow to the brain increased. Neurons fired faster. The effects were real and measurable.
The improvement happens because EPA starts working quickly. It reduces inflammation in brain tissue. Less swelling means better blood flow. Better blood flow means more oxygen and nutrients reach your neurons.
Week 4: a sharper memory
By the fourth week, memory tests showed clear gains. People remembered names better. They recalled details faster. They made fewer mistakes on mental tasks.
Here’s why: omega-3s help build new connections between brain cells. They strengthen the signals that form memories. They protect the pathways that retrieve stored information.
A 2013 analysis looked at 12 studies on omega-3 and memory. Researchers found that doses around 1.73 grams per day showed a reduction in memory decline rate. The effect was small but consistent. And it built over time.
DHA plays the starring role here. It makes up a huge part of the synapses — the junctions where brain cells connect. More DHA means stronger, more reliable connections.
Week 8 and beyond: measurable brain changes
Studies tracking people over weeks and months revealed something remarkable: brain volume increased in key areas. The hippocampus — your memory center — showed the most growth.
This isn’t just better performance. It’s physical change.
A 2022 study examined 40 older adults with an average age of 76. Scientists measured their omega-3 levels and did brain scans. People with higher EPA and DHA levels had greater brain volume in certain regions. They also scored better on memory and processing speed tests.

The brain can grow new cells throughout life. This process, called neuroplasticity, slows as we age. But omega-3s seem to rev it back up. They provide the raw materials for new neurons. They reduce inflammation that blocks growth. They protect existing cells from damage.
Long-term brain benefits
Protection against cognitive decline
Keep taking omega-3s, and the benefits compound.
A 2024 analysis examined 24 studies with nearly 10,000 adults over age 40. The studies lasted from 3 to 36 months. Researchers found that people taking more than 500 mg of omega-3 daily showed better executive function. That’s your ability to plan, focus, and switch between tasks.

The benefit appeared within the first year. It continued as long as people kept taking the supplements. The effect was stronger when daily EPA intake was higher.
Another review in 2023 looked at fish intake and cognitive decline. People who ate fish regularly or took omega-3 supplements had a lower risk of mild cognitive impairment. That’s the fuzzy thinking that often comes before serious memory problems.
But here’s the catch: the protection doesn’t extend to all conditions. The same research found benefits in mild cognitive impairment but not in Alzheimer’s disease. Once severe damage occurs, omega-3s can’t reverse it. They help prevent the damage from starting.

A brighter mood
Your brain uses omega-3s for more than memory. They affect mood too.
EPA in particular helps regulate neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. Low omega-3 levels link to higher rates of anxiety and low mood. Some studies suggest that omega-3 supplements can ease mild symptoms, though they’re not a replacement for treatment.
Think of it as brain maintenance. You can’t pour fuel into an empty tank and expect peak performance.
Anti-aging effects
Aging brains face two main threats: swelling and oxidative stress. Both damage cells over time.
Omega-3s fight both problems. They calm inflammation throughout the nervous system. They act as antioxidants, mopping up harmful molecules before they can damage DNA. They keep blood vessels healthy, ensuring a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients.
This isn’t about living forever. It’s about keeping your brain sharp for as long as possible.
Who benefits most?
Not everyone sees the same results from omega-3 supplements. Here’s who tends to benefit most:
Older adults (65+) show the strongest cognitive benefits. Their brains have more inflammation and oxidative stress. Omega-3s target both problems.
People with mild cognitive impairment see measurable improvements. If you’ve noticed your memory slipping, omega-3s might help slow or stop the decline.
Those with low baseline levels benefit most dramatically. If you rarely eat fish, you’ll likely notice bigger changes than someone who already eats salmon twice a week.
Younger adults may see focus and mood improvements but less dramatic cognitive changes. Your brain is already functioning well. Omega-3s help maintain that state.
People with the APOE4 gene variant (a risk factor for Alzheimer’s) may need higher doses. Some research suggests they need 2,000 mg or more daily to see benefits.
How much and when: your dosage guide
Different timelines require different approaches. Here’s what the research shows:
| Timeline | Daily Dosage | Expected Benefits | Study Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-4 weeks | 500-1,000 mg | Improved focus, mental clarity, better blood flow | Short-term studies on learning and memory |
| 4-8 weeks | 1,000-2,000 mg | Better memory recall, faster processing | Multiple controlled trials |
| 3-6 months | 500+ mg | Enhanced executive function, sustained cognitive gains | 2024 meta-analysis of 24 studies |
| 12+ months | 500-2,000 mg | Reduced cognitive decline risk, maintained brain volume | Long-term observational studies |
Start at the lower end. Give it at least 4-8 weeks. Increase the dose if you don’t notice improvements after two months.
Most studies showing cognitive benefits used doses between 500 mg and 2,000 mg per day. Going higher doesn’t necessarily work better. In fact, the 2013 analysis found that doses above 1.73 grams per day showed less benefit than lower doses.
How to get your daily dose: a practical guide
Food first
The best omega-3 sources swim in cold water. Here’s a complete breakdown:
| Food Source | Serving Size | Omega-3 Content (mg) | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atlantic Salmon (wild) | 3 oz | 1,500-2,000 | DHA/EPA |
| Mackerel | 3 oz | 1,000-1,500 | DHA/EPA |
| Sardines (canned) | 3 oz | 1,000-1,200 | DHA/EPA |
| Anchovies | 3 oz | 1,200-1,400 | DHA/EPA |
| Herring | 3 oz | 1,500-2,000 | DHA/EPA |
| Trout (rainbow) | 3 oz | 900-1,000 | DHA/EPA |
| Flaxseeds (ground) | 2 tbsp | 3,200 | ALA |
| Chia Seeds | 2 tbsp | 2,500 | ALA |
| Walnuts | 1/4 cup | 2,500 | ALA |
| Hemp Seeds | 3 tbsp | 2,600 | ALA |
Aim for two servings of fatty fish per week. That’s the minimum for brain health. Three to four servings provide even better protection.
🧠 Omega-3 Intake Calculator
Track your weekly omega-3 consumption and get personalized recommendations
🐟 Fatty Fish (per week)
🌱 Plant-Based Sources (per week)
💊 Supplements (daily)
Your Results
Brain-healthy recipes
Quick Salmon Bowl
Mix 4 oz grilled salmon with 1 cup quinoa, half an avocado, and mixed greens. Drizzle with olive oil and lemon. Add sliced cucumber and cherry tomatoes.
Total omega-3s: about 1,800 mg DHA/EPA
Prep time: 15 minutes
Morning Brain Boost Smoothie
Blend 2 tbsp ground flaxseed, 1 cup blueberries, 1 banana, 1 tbsp almond butter, and 1 cup almond milk. Add a handful of spinach. Blend until smooth.
Total ALA: about 3,200 mg
Prep time: 5 minutes
Mediterranean Sardine Toast
Mash 3 oz sardines with a squeeze of lemon and black pepper. Spread on whole grain toast. Top with sliced tomatoes and fresh basil. Add a drizzle of olive oil.
Total omega-3s: about 1,100 mg DHA/EPA
Prep time: 5 minutes
Plant-based options: making them work
If you don’t eat fish, you face a challenge. ALA conversion to DHA and EPA is inefficient. But you can improve it.
Conversion boosters:
- Limit omega-6 intake (vegetable oils, processed foods)
- Ensure adequate B vitamins, zinc, and magnesium
- Avoid trans fats (they block conversion)
- Consider algae oil supplements
Algae oil offers a plant-based source of DHA. It comes from the same algae that fish eat. A typical dose provides 300-600 mg of DHA per serving. It works just as well as fish oil.
Best approach for plant-based eaters: Combine ALA-rich foods daily with an algae oil supplement. Eat 2 tbsp ground flaxseed plus take 300-500 mg algae DHA. This covers your bases.
Supplementing smartly
Can’t eat fish twice a week? Supplements help fill the gap.
Look for combined DHA and EPA. A good ratio is about 2:1 DHA to EPA, though any combination works. Total daily dose should hit at least 500 mg, preferably 1,000-2,000 mg for brain benefits.
Check for purity. Fish oil can contain pollutants. Look for brands that test for mercury, PCBs, and other toxins. Third-party certification from groups like USP, IFOS, or NSF ensures quality.
Consider the form. Triglyceride form absorbs better than ethyl ester form. Look for “re-esterified triglycerides” or “triglyceride form” on the label. This matters more than you’d think — triglyceride form absorbs about 70% better.
Krill oil offers another option. It contains omega-3s bound to phospholipids, which may absorb even better than triglycerides. But it’s more expensive and provides less total omega-3 per capsule.
How to maximize absorption
Many people take supplements wrong. This reduces effectiveness by half or more.
Take with fatty meals. Omega-3s need fat to absorb properly. Taking them with breakfast eggs or lunch with olive oil increases absorption by up to three times compared to taking them on an empty stomach.
Avoid fiber supplements at the same time. Fiber can bind to fats and reduce absorption. Space them out by at least two hours.
Split larger doses. Taking 1,000 mg twice daily works better than 2,000 mg once. Your body can only absorb so much at once.
Store properly. Omega-3s oxidize easily. Keep bottles in the fridge after opening. Use within three months. Check the smell — rancid oil smells fishy and can actually harm you.
| Storage Factor | Why It Matters | Best Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Light exposure | Breaks down fatty acids | Dark bottles only |
| Heat | Speeds oxidation | Store in fridge after opening |
| Air | Causes rancidity | Keep tightly sealed |
| Freshness date | Potency decreases | Use within 3 months of opening |
| Smell test | Rancid oil = harmful | Should smell mild, not fishy |
Testing your omega-3 levels
Want to know where you stand? You can measure it.
The Omega-3 Index blood test measures EPA and DHA in your red blood cells. It shows how much actually made it into your tissues.
Target range: 8-12% for optimal brain health
Current average: Most Americans sit at 4-5%
You can order this test through your doctor or use at-home test kits. Test your baseline. Take supplements for 3-4 months. Test again to see if you’re absorbing them properly.
If your levels don’t rise, you might need to:
- Increase your dose
- Switch supplement forms (try triglyceride if you’re using ethyl ester)
- Take with fattier meals
- Reduce omega-6 intake
Common mistakes people make
Avoid these pitfalls:
Buying oxidized supplements. Cheap brands often use rancid oil. It not only doesn’t work — it can increase inflammation. Always check third-party testing.
Taking on an empty stomach. You’ll absorb maybe 20% of the dose. Always take with food containing fat.
Expecting overnight results. Brain changes take weeks. Give it at least 4-8 weeks before deciding if it works.
Skipping consistency. Benefits require daily intake. Taking omega-3s sporadically won’t help your brain.
Ignoring EPA/DHA content. Some supplements list total omega-3s but contain mostly filler oils. Check the label for actual EPA and DHA amounts.
Not checking for contaminants. Fish oil can concentrate toxins. Only buy supplements tested for heavy metals and PCBs.
Thinking more is always better. Studies show diminishing returns above 2,000 mg daily. Higher doses also increase bleeding risk.
Safety and side effects
Omega-3 supplements are safe for most people. But you should know the risks.
Common side effects:
- Fishy aftertaste or burps (take with food, freeze capsules, or switch to enteric-coated)
- Mild digestive upset (take with meals, reduce dose temporarily)
- Loose stools (usually with doses above 3,000 mg)
Blood-thinning properties: Omega-3s thin your blood slightly. This is usually helpful. But if you take blood thinners like warfarin, aspirin, or clopidogrel, talk to your doctor first. You may need dose adjustments.
Maximum safe dose: Most studies use up to 3,000 mg daily without problems. The FDA says up to 5,000 mg is “generally recognized as safe.” But stick to 2,000 mg or less unless your doctor advises otherwise.
Pregnancy and nursing: Pregnant women need 200-300 mg of DHA daily. It supports fetal brain growth. Studies show it may also reduce the risk of postpartum mood issues. But avoid high-mercury fish. Stick to supplements or low-mercury options like salmon and sardines.
Children: Kids need omega-3s for brain growth. Many children’s supplements provide 200-500 mg. Check with your pediatrician for proper dosing.
When to talk to a doctor:
- You take blood-thinning medication
- You have a bleeding disorder
- You’re scheduled for surgery (stop omega-3s 1-2 weeks before)
- You have a fish or shellfish allergy (try algae oil instead)
- You’re pregnant or nursing
Omega-3 supplements vs. other options
How do omega-3s compare to other brain health approaches?
| Intervention | Cognitive Benefit | Side Effects | Monthly Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 supplements | Mild to moderate | Minimal | $10-30 |
| Prescription cognitive enhancers | Moderate | Significant | $200-400 |
| Exercise (regular aerobic) | Moderate to strong | None (positive) | $0-50 |
| Mediterranean diet | Moderate to strong | None (positive) | Variable |
| Cognitive training | Mild | None | $0-30 |
The best approach? Combine them. Take omega-3s, exercise regularly, eat well, and stay mentally active. Each adds to the others.
Special considerations: pregnancy and child development
Brain development doesn’t stop at birth. Omega-3s play a huge role in early life.
During pregnancy: The fetus pulls DHA from the mother’s stores. Women need at least 200-300 mg of DHA daily. Low levels link to:
- Lower IQ in children
- Behavioral problems
- Vision issues
- Increased risk of preterm birth
After birth: Breast milk contains DHA if the mother has adequate intake. Formula companies now add it too. But levels vary widely.
In childhood: Studies link higher omega-3 intake to:
- Better reading skills
- Improved attention
- Fewer behavioral problems
- Better sleep
Children’s supplements typically provide 200-500 mg. Gummy versions are popular but check the actual omega-3 content — some contain very little.
Conclusion
The research paints a clear picture: your brain can change. It can grow. It can improve. Even in adulthood.
Omega-3 fatty acids give your brain what it needs to stay sharp. They build cell membranes. They reduce inflammation. They protect against age-related decline. And they work fast — improvements start within weeks.
You don’t need a prescription. You don’t need expensive treatments. You need fatty fish twice a week or a quality supplement daily.
Your memory at 70 depends on choices you make today. Feed your brain well. Give it the fats it craves. Watch as the fog lifts, focus sharpens, and mental clarity returns.
Studies involving thousands of people show the same thing: people who consume adequate omega-3s maintain better brain function as they age. They remember more. They think faster. They stay independent longer.
The research is clear. The benefits are real. The choice is yours.
FAQs
How long does it take for omega-3 to improve brain function?
Most people notice subjective improvements (focus, mental clarity) within 2-4 weeks. Measurable changes in memory and executive function typically appear after 4-12 weeks of consistent use. Long-term brain protection requires ongoing intake.
What’s the best omega-3 supplement for brain health?
Look for a supplement with at least 500 mg combined EPA and DHA in triglyceride form. It should be third-party tested for purity (USP, IFOS, or NSF certification). A 2:1 ratio of DHA to EPA works well for brain health. Popular brands that meet these criteria include Nordic Naturals, Sports Research, and Viva Naturals.
Can omega-3 prevent Alzheimer’s?
Omega-3s may reduce the risk of mild cognitive impairment, which sometimes leads to Alzheimer’s. But research shows they don’t reverse or treat Alzheimer’s once it develops. Think of them as prevention, not treatment. Start early for best results.
Is fish oil or krill oil better for the brain?
Both work. Krill oil may absorb slightly better due to its phospholipid structure. But fish oil provides more omega-3s per capsule and costs less. For most people, a quality fish oil supplement is the better value. If you have trouble absorbing fats, krill oil might work better.
Do I need omega-3 supplements if I eat fish twice a week?
Probably not. Two servings of fatty fish provide about 3,000-4,000 mg of omega-3s weekly — more than enough for brain health. But if you eat leaner fish (tilapia, cod) or smaller portions, supplements can help fill the gap. Test your Omega-3 Index if you’re unsure.
Can I take too much omega-3?
Yes. Doses above 3,000 mg daily can increase bleeding risk. Very high doses may also suppress immune function slightly. Most studies show benefits max out around 2,000 mg daily. More isn’t better.
What about omega-3-enriched foods like eggs and milk?
They help but don’t provide huge amounts. An omega-3 egg contains about 100-150 mg. Fortified milk has about 30-50 mg per cup. You’d need to eat a lot to hit daily targets. They’re nice additions but not replacements for fish or supplements.


