What does science actually say about immune supplements? We searched for clinical trials on eight popular supplements. Some live up to the hype, others not so much.
Quick Reference Guide: Supplements at a Glance
| Supplement | Best For | Research-Backed Dosage | When to Take | Evidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D | People with deficiency (<25 nmol/L) | 400-2000 IU daily | With fat-containing meals | Strong |
| Zinc | Early cold symptoms (<24 hours) | 75-100 mg daily (lozenges) | At first symptom | Moderate |
| Vitamin C | Athletes, high-stress populations | 200-500 mg daily | Daily for prevention | Moderate |
| Probiotics (LGG, BB-12) | Frequent respiratory infections | 1-10 billion CFU daily | Daily with meals | Moderate |
| Elderberry | Active cold/flu symptoms | 300-600 mg extract daily | During illness only | Limited |
| Echinacea | Not consistently effective | Varies widely | Not recommended | Weak |
| Curcumin | Anti-inflammation support | 500-1000 mg daily | With black pepper | Limited |
| Selenium | Known deficiency | 55-200 mcg daily | With meals | Limited |
1. Vitamin D
The Claim: It’s the ultimate immune defender.
The Science: A major systematic review looked at 46 trials with 64,086 people. The results showed about an 8% lower risk of respiratory infections.
That sounds modest. But here’s where it gets interesting.
The Catch: The benefit isn’t equal for everyone.
A 2024 analysis found people with very low vitamin D levels (under 25 nmol/L) got the biggest protection. If your levels are already good then the effect drops off fast.
Think of it like filling a gas tank. If you’re on empty, adding fuel makes a huge difference. If you’re already full, more doesn’t help.

Who Benefits Most from Vitamin D?
Research shows these groups see the strongest effects:
- People with confirmed deficiency
- Those who rarely see winter sun
- People with darker skin (need more sun for same production)
- Adults over 65 (skin produces less with age)
- People with conditions affecting absorption (Crohn’s, celiac disease)
Warning Signs You Might Be Deficient
Most people with low vitamin D feel nothing. But watch for these clues:
- Constant tiredness that rest doesn’t fix
- Muscle weakness or aches
- Bone pain, especially in your lower back
- Getting sick often
- Mood changes or feeling down
- Slow wound healing
Absorption Tip: Timing Matters
Vitamin D is fat-soluble. Take it with foods containing healthy fats for best absorption. Good options include:
- Avocado on toast
- A handful of nuts
- Salmon or other fatty fish
- Full-fat yogurt
- Eggs
What This Means for You
Get your levels checked first. A simple blood test tells you if you need it. The test costs $30-50 without insurance.
Focus on these before buying pills:
- Get outside when the sun’s out (10-15 minutes daily)
- Eat fatty fish like salmon twice weekly
- Try fortified milk or cereal
- Consider an egg for breakfast
Research shows daily doses between 400-2000 IU work best for most people. Skip the mega-doses. They don’t add extra protection.
Quality Check: Look for third-party testing seals (USP, NSF, ConsumerLab). These verify what’s on the label matches what’s in the bottle.
2. Zinc
The Claim: It’s your go-to when you feel a cold coming.
The Science: Zinc plays a key role in immune cell function. A 2022 meta-analysis of zinc supplementation found it supports production of T-cells and natural killer cells. Without enough zinc, your immune system can’t work right.
The Catch: Timing is everything. The research is clear on this one.
Zinc might shorten a cold’s length by 1-2 days. But only if you take it within 24 hours of first symptoms. Wait too long? You’ve missed the window.
A study with 281 participants found those taking zinc lozenges had colds lasting 4.5 days versus 8 days for placebo. That’s nearly half the time.

Who Benefits Most from Zinc?
These groups may need extra attention to zinc levels:
- Vegetarians and vegans (plant sources less absorbed)
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
- People with digestive disorders
- Older adults (absorption decreases with age)
- Anyone with frequent infections
Zinc Lozenges vs. Pills: The Form Matters
Lozenges work better than pills for colds. Why? They coat your throat where viruses take hold. The direct contact matters.
Pills work fine for daily supplementation to correct deficiency. But for cold treatment? Stick with lozenges.
Warning: Don’t Overdo It
Taking high doses of zinc (over 100 mg daily) for too long can cause problems:
- Copper deficiency
- Nausea
- Weakened immunity (ironic, right?)
- Reduced sense of taste or smell
Stick to recommended doses and only use high amounts for short periods.
What This Means for You
Think of zinc as a quick-response tool, not a shield.
Keep some lozenges at home. Start them fast when you feel that first tickle in your throat. Take 75-100 mg daily (in divided doses) for 5-7 days.
Don’t take zinc lozenges daily long-term. They’re for acute use only.
Food Sources vs. Supplement Forms
| Food Source | Zinc Content | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Oysters (3 oz) | 74 mg | Best natural source |
| Beef (3 oz) | 7 mg | Highly absorbable |
| Pumpkin seeds (1 oz) | 2.2 mg | Good plant source |
| Cashews (1 oz) | 1.6 mg | Easy snack option |
| Chickpeas (½ cup) | 1.3 mg | Combine with vitamin C for better absorption |
3. Vitamin C
The Claim: It’s the classic cold fighter. Pop some at the first sniffle.
The Science: Studies show it can shorten cold length by about 8%. That’s roughly one day off a typical cold.
Not nothing. But not magic either.
The Catch: Here’s the big surprise. Vitamin C doesn’t prevent colds for most people.
The exception? People under extreme stress. Marathon runners saw their cold risk cut nearly in half. Same for soldiers in harsh conditions.
For the rest of us sitting at desks? The preventive effect is tiny to none.

Who Benefits Most from Vitamin C?
Research shows clear benefits for:
- Endurance athletes during training
- People in extreme cold conditions
- Those under severe physical stress
- Smokers (need more due to oxidative stress)
For everyone else, vitamin C helps you recover slightly faster. But it won’t keep you from getting sick.
The Absorption Truth
Your body can only absorb about 200-500 mg of vitamin C at once. The rest? You pee it out.
Those 1000 mg pills? Mostly wasted money.
Better approach: Split doses throughout the day if you take supplements. Or better yet, get it from food.
What This Means for You
Don’t expect miracles. Vitamin C might help you recover a bit faster once you’re sick. But it won’t keep you from getting sick in the first place.
Save your money on daily high-dose pills. Eat an orange instead. You’ll get the vitamin plus fiber and other good stuff.
Smart Combination: Taking vitamin C with zinc may help zinc absorption. The two work well together during a cold.
Vitamin C Power Smoothie Recipe
This simple smoothie packs vitamin C and zinc together for better absorption.
Ingredients:
- 1 cup strawberries (fresh or frozen)
- 1 kiwi, peeled
- ½ cup orange juice
- ½ cup Greek yogurt
- 1 tablespoon hemp seeds (zinc source)
- 1 teaspoon honey
- Handful of ice
Instructions: Blend all ingredients until smooth. Drink within 30 minutes for maximum vitamin C content. Makes 1 serving.
Nutrition highlight: Provides about 200 mg vitamin C and 2 mg zinc, plus probiotics from yogurt.
4. Probiotics
The Claim: A healthy gut equals a healthy immune system.
The Science: Research on roughly 8,000 people showed promise. Probiotics reduced both how often people got respiratory infections and how long they lasted.
One study with college students found those taking specific probiotic strains had colds that were 2 days shorter. Their symptom severity dropped by 34%.
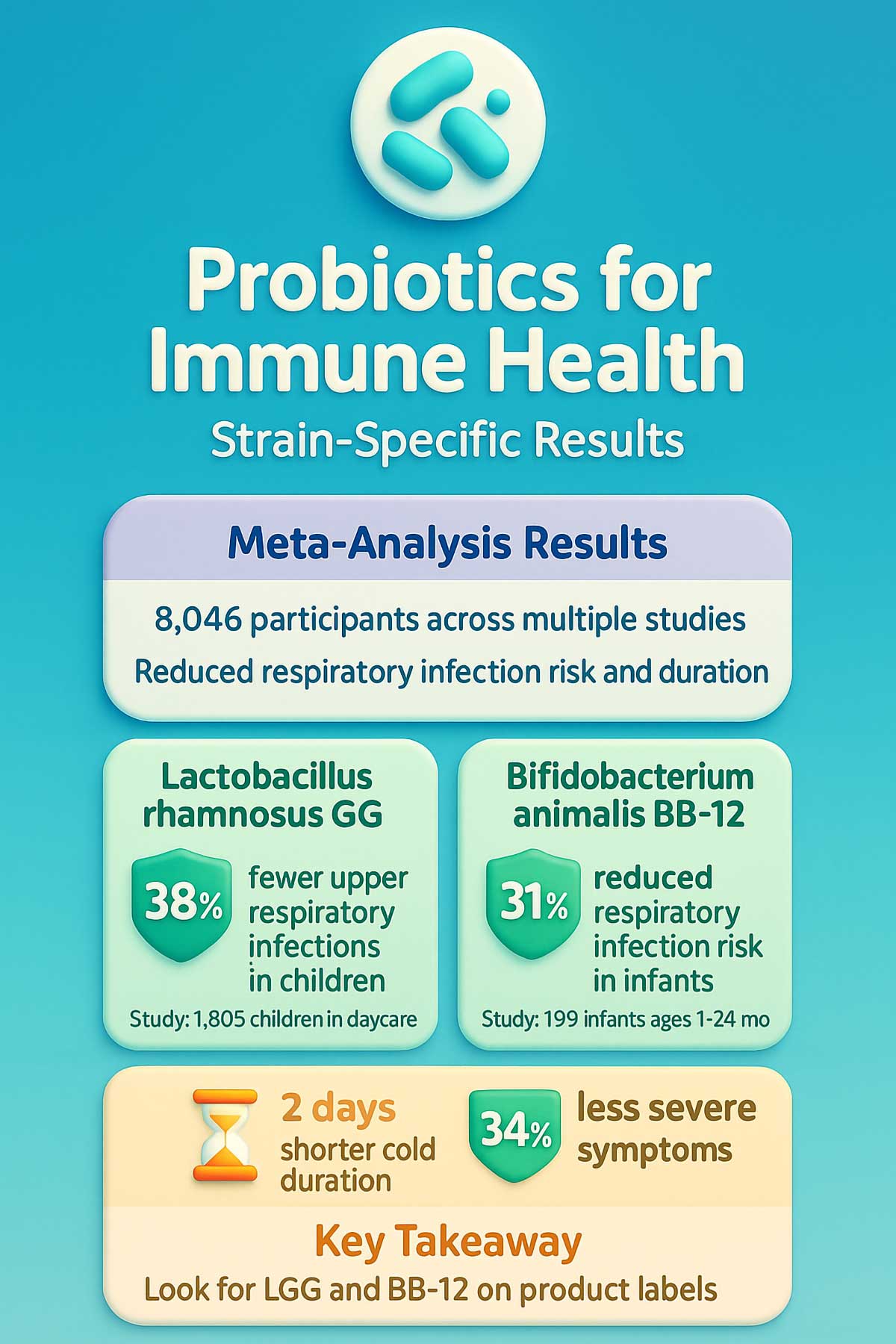
The Catch: Not all probiotics are created equal. This is huge.
The term “probiotic” is very broad. Different strains do different things. A generic probiotic might not help your immune system at all.
Research-Backed Probiotic Strains for Respiratory Health
| Strain | Specific Benefits | Typical Dosage | Study Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) | Reduced upper respiratory infections by 38% in children | 1-10 billion CFU | Children in daycare, 1,805 participants |
| Bifidobacterium animalis BB-12 | Reduced respiratory infection risk by 31% in infants | 10 billion CFU | Infants 1-24 months, 109 participants |
| LGG + BB-12 combined | Shortened cold duration by 2 days, reduced severity by 34% | 1 billion CFU each | College students, 198 participants |
| Lactobacillus casei Shirota | Enhanced natural killer cell activity | 6.5 billion CFU | Healthy adults |
| Bifidobacterium longum | Reduced incidence of common cold by 27% | 1 billion CFU | Healthy adults |
The Gut-Lung Axis: How It Works
Your gut and lungs talk to each other. Here’s how probiotics help:
- They strengthen your intestinal barrier
- This reduces inflammation throughout your body
- They train immune cells in your gut
- These cells then travel to your lungs
- Your respiratory tract becomes more resistant to infection
A fascinating study followed 281 children in daycare. Those receiving Lactobacillus GG had 38% fewer upper respiratory infections. They also needed fewer antibiotics.
Who Benefits Most from Probiotics?
Research shows stronger effects for:
- Children in daycare or school (high exposure)
- College students in dorms
- People with frequent respiratory infections (4+ per year)
- Anyone taking antibiotics
- People with digestive issues
What This Means for You
Read labels carefully. Look for products listing the exact strains tested in research.
Generic “probiotic blend” products? They’re a gamble. You might get the helpful strains. You might not.
Look for these on the label:
- Strain name (not just “Lactobacillus”)
- CFU count (colony-forming units)
- Expiration date
- Storage requirements
Eating yogurt with live cultures can help too. Just check that it contains active strains. Labels should say “contains live and active cultures.”
Storage Tip: Most probiotics need refrigeration. Heat kills the beneficial bacteria. Keep them cool.
Probiotic-Rich Immune Bowl Recipe
Start your day with this breakfast that combines multiple immune-supporting nutrients.
Ingredients:
- 1 cup plain Greek yogurt (look for live cultures)
- ½ cup overnight oats (prepared night before)
- 1 tablespoon pumpkin seeds (zinc)
- ½ cup mixed berries (vitamin C)
- 1 tablespoon ground flax (omega-3s)
- 1 teaspoon honey
- Sprinkle of cinnamon
Instructions: Layer ingredients in a bowl. The probiotic yogurt provides beneficial bacteria. Berries add vitamin C. Pumpkin seeds supply zinc. The combination works together to support immune function.
Prep tip: Make overnight oats by mixing ½ cup oats with ½ cup milk. Refrigerate 8 hours.
5. Elderberry
The Claim: It’s nature’s flu fighter.
The Science: One solid study followed 312 airline passengers. Those taking elderberry extract had colds that were two days shorter. Their symptoms were less harsh too.
Symptoms improved by 50% faster compared to placebo.

The Catch: Here’s something odd. Early in the pandemic, some worried elderberry might over-stimulate the immune system. The concern? A “cytokine storm.”
For common colds and flu in healthy people, this fear hasn’t panned out. But it shows that “natural” doesn’t mean weak or harmless.
Who Should Avoid Elderberry?
Most healthy people can use elderberry safely. But avoid it if you:
- Have autoimmune conditions (talk to your doctor first)
- Are pregnant or breastfeeding (not enough safety data)
- Take immunosuppressant drugs
- Have severe allergies
Form and Dosage Guidance
Elderberry comes in several forms:
- Syrup: 1-2 tablespoons daily
- Capsules: 300-600 mg extract daily
- Lozenges: Follow package directions
- Gummies: Check for actual elderberry content (many have minimal amounts)
What This Means for You
Use elderberry when you’re already sick. It might ease symptoms and speed recovery.
Don’t take it daily as a preventive. We don’t have good data supporting that approach.
Start it at symptom onset. Then stop when you feel better.
Quality matters: Look for standardized elderberry extract. Some products contain very little actual elderberry.
6. Echinacea
The Claim: It’s an herbal staple for staying healthy.
The Science: People have used echinacea for years. Some studies show a slight benefit. Many show none at all.
A systematic review looked at multiple trials. Results were all over the map. Some showed 10-15% reduction in cold risk. Others showed zero effect.
The Catch: “Echinacea” can mean many things. Different species of the plant. Different parts (root, leaf, flower). Each might work differently.
This lack of standard products explains the wild variation in results. One bottle might help. Another might do nothing.

Why Results Vary So Much
Three species are commonly used:
- Echinacea purpurea (most studied)
- Echinacea angustifolia
- Echinacea pallida
Products may use:
- Root only
- Aerial parts only
- Whole plant
- Different extraction methods
Without knowing exactly what you’re getting, predicting results is impossible.
What This Means for You
The science here is too shaky to recommend strongly. Other supplements on this list have much stronger backing.
If you want to try it, fine. Just don’t expect reliable results. And don’t skip better options for it.
Better strategy: Focus on vitamin D, zinc, and probiotics. These have consistent evidence behind them.
7 & 8 Curcumin and Selenium
The Claim: They’re often in “immune-boosting” formulas.
The Science: Curcumin fights inflammation hard. It blocks several inflammatory pathways in the body. Selenium helps immune cells work properly. Both matter for health.
The Catch: Being important doesn’t mean supplementing helps prevent infections.
The human trials are weak. Yes, these nutrients support your immune environment. But studies showing they stop or treat colds are missing.
Selenium matters most when you’re deficient. Same basic idea as vitamin D. If you have enough, more doesn’t help.
Curcumin: The Absorption Challenge
Curcumin is poorly absorbed on its own. Your body breaks it down quickly.
Solutions that help:
- Take with black pepper (increases absorption by 2000%)
- Use with healthy fats
- Look for formulations with enhanced absorption (liposomal, phytosome)
Without these tricks, most curcumin passes right through you.
Selenium: Easy to Get from Food
Just two Brazil nuts give you a full day’s selenium. Seriously. It’s that easy.
More isn’t better with selenium. High doses (over 400 mcg daily) can cause:
- Hair loss
- Nail brittleness
- Nausea
- Irritability
Stick to food sources unless you have confirmed deficiency.
What This Means for You
Get these from food first.
For curcumin: Cook with turmeric. Add black pepper to boost absorption. Try it in:
- Curry dishes
- Golden milk (turmeric latte)
- Smoothies
- Scrambled eggs
For selenium: Eat a couple Brazil nuts. That’s all you need for the day. Other good sources:
- Seafood
- Meat
- Whole grains
- Eggs
Don’t buy expensive supplements unless you have a known deficiency.

Golden Milk Recipe (Curcumin + Absorption Boosters)
This traditional drink maximizes curcumin absorption.
Ingredients:
- 2 cups milk (dairy or plant-based)
- 1 teaspoon ground turmeric
- ½ teaspoon ground cinnamon
- ¼ teaspoon ground ginger
- Pinch of black pepper (crucial for absorption)
- 1 teaspoon honey
- 1 teaspoon coconut oil (fat helps absorption)
Instructions: Heat milk in a saucepan over medium heat. Whisk in spices and coconut oil. Simmer 5 minutes. Strain if desired. Add honey. Drink warm before bed.
Why it works: Black pepper contains piperine, which increases curcumin absorption by 2000%. The coconut oil provides fat for better uptake.
Supplements That Work Better Together
Some nutrients team up for stronger effects. Here are proven combinations:
Vitamin D + K2 + Magnesium
- Vitamin D needs magnesium to activate
- Vitamin K2 directs calcium to bones (not arteries)
- Take all three for best bone support
Zinc + Vitamin C
- Vitamin C may help zinc absorption
- Both fight cold viruses through different mechanisms
- Take together at first cold symptoms
Probiotics + Prebiotics
- Prebiotics feed your probiotic bacteria
- Together, they colonize your gut better
- Look for “synbiotic” formulas or eat fiber-rich foods with probiotics
Iron + Vitamin C (If You Need Iron)
- Vitamin C dramatically increases iron absorption
- Important for people with anemia
- Take vitamin C with iron-rich meals
Warning: Some combinations can cause problems. Calcium blocks iron absorption. Zinc blocks copper. Space these out by several hours.
Supplement Interaction Checker
Select your supplements and medications to check for interactions
Select Supplements
Common Medications (Optional)
Who Benefits Most? Population-Specific Recommendations
| Population | Top Priority Supplements | Why They Help | Testing Recommended |
|---|---|---|---|
| Athletes/Very Active | Vitamin C (500 mg), Probiotics | Extreme stress increases infection risk 50% | Vitamin D levels |
| Elderly (65+) | Vitamin D (800-1000 IU), Probiotics | Immune function declines with age | Vitamin D, zinc levels |
| Children in Daycare | Probiotics (LGG), Vitamin D | High exposure environment | Vitamin D only |
| Frequent Travelers | Probiotics, Elderberry (during illness) | Stress, close quarters, new exposures | Vitamin D |
| People with Deficiency | Vitamin D, Zinc | Correcting deficiency has strongest evidence | All relevant nutrients |
| General Population | None (unless deficient) | Most people don’t need supplements with good diet | Consider vitamin D in winter |
Self-Assessment: Do You Need Immune Supplements?
Answer these questions to identify which supplements might help you:
Vitamin D Questions:
- Do you spend most of your time indoors?
- Do you live in a northern climate with limited winter sun?
- Do you have darker skin?
- Do you rarely eat fatty fish or fortified foods?
- Do you feel tired often despite good sleep?
Score: 3+ yes answers suggest getting vitamin D levels tested.
Zinc Questions:
- Are you vegetarian or vegan?
- Do you get sick often (4+ times per year)?
- Do you have digestive issues?
- Are you over 65?
- Do your wounds heal slowly?
Score: 3+ yes answers suggest checking zinc status or trying zinc at first cold symptoms.
Probiotic Questions:
- Do you catch every cold going around?
- Have you taken antibiotics in the past 3 months?
- Do you have digestive issues?
- Are you in a high-exposure environment (school, healthcare, public transit)?
- Do you rarely eat fermented foods?
Score: 3+ yes answers suggest trying research-backed probiotic strains.
Vitamin C Questions:
- Are you an endurance athlete?
- Do you smoke?
- Are you under extreme physical stress?
- Do you live in very cold conditions?
Score: 2+ yes answers suggest vitamin C supplementation (500 mg daily).
When Supplements Can’t Help: Know the Red Flags
Supplements support immune health. They don’t treat serious infections. See a doctor if you have:
Immediate medical attention needed:
- Fever over 103°F (39.4°C)
- Difficulty breathing or chest pain
- Severe headache with stiff neck
- Confusion or disorientation
- Symptoms that rapidly worsen
Schedule a doctor visit for:
- Fever lasting more than 3 days
- Symptoms that don’t improve after 10 days
- Recurring infections (more than 4-6 per year)
- Green or bloody mucus
- Severe sore throat with white patches
Why antibiotics vs supplements matter: Viral infections: Supplements might help reduce severity and duration. Antibiotics don’t work.
Bacterial infections: You need antibiotics. Supplements won’t cure bacterial pneumonia, strep throat, or urinary tract infections.
Don’t delay medical care hoping supplements will fix serious infections.
Testing Before Supplementing: Know Your Numbers
Smart supplementation starts with knowing what you actually need.
Tests Worth Requesting
Vitamin D (25-hydroxyvitamin D):
- Cost: $30-50 without insurance
- Normal range: 30-50 ng/mL
- Deficient: Below 20 ng/mL
- Test frequency: Once yearly, or 3 months after starting supplements
Zinc:
- Cost: $20-40
- Normal range: 60-120 mcg/dL
- Not routinely tested (symptoms usually indicate need)
Complete Blood Count (CBC):
- Checks for anemia (may indicate iron, B12, folate needs)
- Often covered by insurance
- Shows if frequent infections relate to blood cell issues
When Testing Makes Sense
Test if you:
- Have symptoms of deficiency
- Are in a high-risk group
- Take supplements regularly (check if they’re working)
- Get sick very often
- Before starting high-dose supplements
Don’t test if:
- You eat a varied diet and feel fine
- You’re trying low-dose supplements (under 100% DV)
- You had recent normal results
Understanding Your Results
Vitamin D interpretation:
- Under 12 ng/mL: Severely deficient (need prescription-dose treatment)
- 12-20 ng/mL: Deficient (need supplementation)
- 20-30 ng/mL: Insufficient (may benefit from supplementation)
- 30-50 ng/mL: Sufficient (maintain current intake)
- Over 100 ng/mL: Too high (risk of toxicity)
Talk to your doctor about results. They can recommend appropriate dosing based on your specific levels.
3-Day Immune-Supporting Meal Plan
This simple plan naturally incorporates multiple immune-supporting nutrients.
Day 1
Breakfast: Probiotic Immune Bowl (recipe above)
- Provides: Probiotics, vitamin C, zinc
Lunch: Salmon salad with spinach, walnuts, orange segments
- Provides: Vitamin D, omega-3s, vitamin C, iron
Dinner: Chicken stir-fry with broccoli, red peppers, garlic, ginger over brown rice
- Provides: Zinc, vitamin C, anti-inflammatory compounds
Snack: Greek yogurt with berries and 2 Brazil nuts
- Provides: Probiotics, vitamin C, selenium
Day 2
Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with turmeric, black pepper, and sautéed mushrooms
- Provides: Vitamin D, selenium, curcumin
Lunch: Lentil soup with carrots, kale, and a side of fortified whole grain bread
- Provides: Zinc, iron, vitamin D (fortified), vitamin C
Dinner: Grass-fed beef tacos with lots of vegetables, salsa, and fermented sauerkraut
- Provides: Zinc, iron, probiotics, vitamin C
Snack: Orange slices with pumpkin seeds
- Provides: Vitamin C, zinc
Day 3
Breakfast: Golden Milk (recipe above) with whole grain toast and almond butter
- Provides: Curcumin, healthy fats, vitamin E
Lunch: Tuna sandwich on fortified bread with tomato, spinach, and fermented pickles
- Provides: Vitamin D, selenium, iron, probiotics
Dinner: Roasted chicken thighs with sweet potato and Brussels sprouts
- Provides: Zinc, vitamin A, vitamin C, selenium
Snack: Kefir smoothie with strawberries and hemp seeds
- Provides: Probiotics, vitamin C, zinc
Shopping List for 3-Day Plan
Proteins: Salmon, chicken, beef, eggs, lentils, tuna Dairy/Alternatives: Greek yogurt, kefir, milk Vegetables: Spinach, kale, broccoli, red peppers, Brussels sprouts, sweet potato, mushrooms Fruits: Berries, oranges, strawberries Nuts/Seeds: Walnuts, Brazil nuts, pumpkin seeds, hemp seeds, almond butter Pantry: Turmeric, black pepper, garlic, ginger, brown rice, whole grain bread, sauerkraut, pickles
Choosing Quality Supplements: What to Look For
Not all supplements are created equal. Here’s how to spot quality products:
Third-Party Testing Seals
These organizations verify supplement content:
- USP (United States Pharmacopeia): Tests for purity and potency
- NSF International: Verifies ingredients match label
- ConsumerLab: Independent testing service
- Informed Choice: Tests for banned substances (good for athletes)
Products with these seals cost more. But you know you’re getting what you pay for.
Label Red Flags to Avoid
Run from products that:
- Make disease cure claims (“cures colds,” “prevents flu”)
- Use proprietary blends (hiding ingredient amounts)
- Lack specific strain names (for probiotics)
- Have no expiration date
- Promise “miracle” results
- Have incomplete contact information
Good labels include:
- Specific ingredient amounts
- Strain names (for probiotics)
- Clear expiration date
- Batch or lot number
- Contact information
- Supplement Facts panel
- Third-party testing seal
Form Matters
Capsules: Usually best for probiotics (protect from stomach acid)
Tablets: Fine for most vitamins, often cheaper
Lozenges: Best for zinc during colds (throat contact)
Liquid: Good for kids or people with swallowing issues, but shorter shelf life
Gummies: Tasty but often have less active ingredient and more sugar
Storage Requirements
Read the fine print:
- Probiotics: Usually need refrigeration (some shelf-stable versions exist)
- Fish oil/Omega-3s: Refrigerate after opening
- Most vitamins: Cool, dry place away from sunlight
- All supplements: Keep away from heat and moisture (not the bathroom!)
Price Reality Check
Typical monthly costs for quality products:
- Vitamin D: $5-15
- Zinc (for occasional use): $8-12
- Vitamin C: $10-20
- Probiotics: $20-40
- Elderberry: $10-20
- Multi-vitamin with immune support: $15-30
If a price seems too good to be true, it probably is. Very cheap supplements often contain fillers or less bioavailable forms.
Kids vs Adults: Different Needs
Children aren’t just small adults. Their immune needs differ.
Supplement Safety for Children
Generally safe for kids:
- Vitamin D (400-600 IU daily)
- Probiotics (LGG, BB-12 strains studied in children)
- Vitamin C (from food preferred)
Use caution:
- Zinc (easy to overdose in children)
- Elderberry (limited pediatric studies)
- Echinacea (not recommended under 12)
Avoid in children:
- High-dose vitamin C
- Adult-formulated multivitamins
- Products with multiple herbs
Age-Specific Dosing
Infants (0-12 months):
- Vitamin D: 400 IU daily (especially if breastfed)
- Probiotics: 1-5 billion CFU (if recommended by pediatrician)
- Don’t give other supplements without doctor approval
Toddlers (1-3 years):
- Vitamin D: 600 IU daily
- Probiotics: 5-10 billion CFU
- No zinc supplements unless deficient
Children (4-8 years):
- Vitamin D: 600 IU daily
- Probiotics: 5-10 billion CFU
- Zinc: Only during illness, reduced dose (follow pediatric guidelines)
Teens (9-18 years):
- Can use adult doses for most supplements
- Still need doctor guidance for high-dose products
Special Considerations for Children
Daycare/School children: Research supports probiotic use (LGG strain). One study found children in daycare taking Lactobacillus GG had 34% fewer infections requiring antibiotics.
Picky eaters: May benefit from vitamin D supplementation. A multivitamin might help fill gaps.
Allergies/Asthma: Some evidence probiotics started early may help. Discuss with pediatrician.
Always: Check with your pediatrician before starting supplements. Children metabolize nutrients differently than adults.
Immune-Supporting Garlic Ginger Soup Recipe
This soup combines research-backed immune supporters in one warming bowl.
Ingredients:
- 2 tablespoons olive oil
- 1 onion, diced
- 6 cloves garlic, minced
- 2 tablespoons fresh ginger, grated
- 8 cups chicken or vegetable broth (bone broth adds extra nutrients)
- 2 carrots, sliced
- 2 celery stalks, sliced
- 1 cup mushrooms, sliced (vitamin D if sun-exposed)
- 2 cups kale or spinach
- 1 cup cooked chicken (optional, for zinc and protein)
- Juice of 1 lemon (vitamin C)
- Salt and pepper to taste
- Red pepper flakes (optional, for circulation)
Instructions:
- Heat olive oil in large pot over medium heat
- Add onion, cook until soft (5 minutes)
- Add garlic and ginger, cook 1 minute until fragrant
- Pour in broth, bring to boil
- Add carrots, celery, mushrooms
- Simmer 15 minutes until vegetables tender
- Add kale and chicken, cook 3 minutes
- Remove from heat, add lemon juice
- Season with salt, pepper, red pepper flakes
Makes 6-8 servings. Store leftovers in fridge for 4 days or freeze for 3 months.
Why it works: Garlic contains allicin with antimicrobial properties. Ginger reduces inflammation. Lemon provides vitamin C. Chicken adds zinc. The warm liquid soothes respiratory passages.
Pro tip: Make a big batch when you feel a cold coming. Eat 1-2 bowls daily during illness.
Your Seasonal Immune Strategy
Adjust your approach throughout the year for best results.
Fall Strategy (September-November)
Priority: Prepare for cold and flu season
Focus on:
- Start vitamin D if you live in northern climates (sun angle too low for skin production)
- Add probiotic if you’re in high-exposure environments (back to school, work after summer)
- Stock zinc lozenges at home
- Get your flu shot
Foods to emphasize:
- Apples and pears (local, in season)
- Winter squash (vitamin A)
- Late-season berries (vitamin C)
Action item: Get vitamin D levels tested now. Start supplementing if under 30 ng/mL.
Winter Strategy (December-February)
Priority: Active defense during peak illness season
Focus on:
- Continue vitamin D (most critical time)
- Use zinc lozenges at first cold symptoms
- Keep elderberry on hand for active infections
- Maintain probiotic routine
Foods to emphasize:
- Citrus fruits (peak season, vitamin C)
- Root vegetables (stored nutrients)
- Fermented foods (sauerkraut, kimchi)
- Fatty fish (vitamin D)
Action item: Track how often you get sick. If it’s more than 3-4 times, consider adding probiotics.
Spring Strategy (March-May)
Priority: Allergy management, transition off winter supplements
Focus on:
- Reduce or stop vitamin D as sun exposure increases
- Continue probiotics if helpful for seasonal allergies
- Focus on whole foods as fresh produce returns
Foods to emphasize:
- Leafy greens (vitamins, minerals)
- Asparagus (prebiotics)
- Strawberries (vitamin C)
- Spring herbs (parsley, cilantro)
Action item: Retest vitamin D levels in late spring. Adjust dosing based on results and sun exposure.
Summer Strategy (June-August)
Priority: Maintain through whole foods and sun exposure
Focus on:
- Most people can stop vitamin D (adequate sun)
- Athletes training hard: consider vitamin C
- Focus on diet over supplements
Foods to emphasize:
- Berries (peak season)
- Tomatoes (lycopene, vitamin C)
- Peppers (vitamin C)
- Stone fruits (vitamins, antioxidants)
Action item: Get outside for 10-15 minutes daily without sunscreen (for vitamin D, then apply sunscreen). This might be enough for many people.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Are Supplements Worth Your Money?
Let’s look at real numbers to help you decide.
Monthly Cost Comparison
| Supplement | Quality Product Cost/Month | Food Source Alternative | Food Cost/Month |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D (1000 IU) | $8-12 | 2 servings fatty fish weekly | $20-30 |
| Zinc (occasional use) | $3-5 (prorated) | Daily pumpkin seeds | $15-20 |
| Vitamin C (500 mg) | $12-18 | 2 oranges daily | $20-30 |
| Probiotics | $25-40 | Daily yogurt with live cultures | $25-35 |
| Elderberry (seasonal) | $5-8 (prorated) | Not available fresh | N/A |
When Supplements Make Financial Sense
Choose supplements if:
- You have confirmed deficiency (vitamin D, zinc)
- Food sources are expensive or unavailable in your area
- You need specific therapeutic doses
- You don’t eat foods containing these nutrients
- You travel often (hard to maintain diet)
Choose food sources if:
- You’re not deficient
- You enjoy eating these foods
- You want additional benefits (fiber, other nutrients)
- You’re on a tight budget (whole foods often cheaper per nutrient)
- You prefer natural approaches
The Hidden Costs
Don’t forget to factor in:
- Doctor visits for testing: $50-150 without insurance
- Blood work: $30-100 per test
- Trying multiple brands: $50-100 wasted on products that don’t work
- Storage requirements: Probiotics need fridge space
The Real ROI (Return on Investment)
Hard to measure but valuable:
- Fewer sick days from work
- Less money on cold medications
- Better quality of life when healthy
- Avoiding antibiotics (which cost money and have side effects)
A study calculated the average cold costs $200-300 in:
- Lost productivity
- Medical care
- Over-the-counter medications
If vitamin D prevents just 1-2 colds per year, it pays for itself.
How to Read Research: Become a Savvy Consumer
Not all studies are created equal. Here’s how to spot reliable research:
What Makes a Study Reliable?
Strong evidence includes:
- Randomized controlled trials (RCTs): Participants randomly assigned to supplement or placebo
- Large sample size: Generally 100+ participants (more is better)
- Proper duration: At least 8-12 weeks for immune effects
- Peer-reviewed: Published in respected journals
- Replicated results: Multiple studies showing similar findings
Weak evidence includes:
- Small studies (under 50 people)
- No control group
- Short duration (under 4 weeks)
- Funded by supplement companies (conflict of interest)
- Only one study showing benefit
Understanding Common Research Terms
Placebo-controlled: Some participants got fake pills. This controls for belief effects.
Double-blind: Neither participants nor researchers knew who got real supplement. This prevents bias.
Statistical significance (p-value): Usually p<0.05 means results unlikely due to chance. Smaller is stronger.
Confidence interval: Range where true effect likely falls. Narrower intervals are better.
Meta-analysis: Combines results from multiple studies. Generally most reliable evidence type.
Red Flags in Research
Be skeptical when you see:
- “Breakthrough” or “miracle” claims
- Results that seem too good to be true
- Only one study supporting claims
- Study funded entirely by product manufacturer
- Results published in obscure journals
- No control group
- Vague outcome measures
Decision-Making Guide: Your Personalized Supplement Plan
Use this simple approach to decide what you actually need.
Step 1: Assess Your Foundation
Before any supplements, rate your basics:
Sleep: Do you get 7-8 hours most nights?
- Yes: Foundation solid
- No: Fix this first (bigger impact than any supplement)
Diet: Do you eat 5+ servings of fruits/vegetables daily?
- Yes: Foundation solid
- No: Improve diet before adding supplements
Stress: Is your stress level manageable?
- Yes: Foundation solid
- No: Address stress (it tanks immunity more than vitamin deficiency)
Exercise: Do you move your body most days?
- Yes: Foundation solid
- No: Start here (moderate exercise boosts immunity)
If you answered “No” to 2+ questions, focus on lifestyle first. Supplements can’t fix a broken foundation.
Identify your risk factors
Check all that apply to you:
Step 3: Make Your Plan
3+ Vitamin D risk factors: Get tested. If deficient (under 30 ng/mL), supplement 1000-2000 IU daily.
3+ Zinc risk factors: Keep zinc lozenges on hand. Take 75-100 mg at first cold symptoms.
3+ Probiotic factors: Try LGG or BB-12 strains for 2-3 months. Track sick days to measure benefit.
2+ Vitamin C factors: Consider 500 mg daily. Most people don’t need this.
Fewer risk factors: Focus on whole foods. Test vitamin D in late winter if concerned.
Step 4: Track and Adjust
Keep a simple log for 3 months:
- Date and supplement taken
- How you feel (energy, mood, digestion)
- Sick days
- Sleep quality
After 3 months, ask:
- Am I getting sick less often?
- Do I feel better?
- Is this worth the cost?
If no clear benefit after 3 months, stop that supplement. Save your money.
Quick Start Guide by Situation
“I get every cold going around” → Start: Probiotic (LGG strain), get vitamin D tested → Cost: $30-40/month
“I work indoors all winter” → Start: Vitamin D test, supplement if low → Cost: $10-15/month
“I feel run down and tired” → Start: Doctor visit, vitamin D test, rule out other causes → Cost: Variable (may not need supplements)
“I want to prevent colds” → Start: Focus on sleep, stress, diet first. Add vitamin D if deficient → Cost: $10/month if supplementing
“I have a cold right now” → Start: Zinc lozenges immediately, elderberry for symptom relief → Cost: $15-20 for acute use
“I’m healthy, just want insurance” → Start: Nothing. Eat well, sleep enough, move daily → Cost: $0
Your Action Plan: Getting Started
Ready to implement what you’ve learned? Follow this roadmap.
Week 1: Assessment Phase
Day 1-2: Complete the self-assessment quiz above. Identify your risk factors.
Day 3-4: Track what you currently eat. Note foods rich in vitamin D, zinc, vitamin C, and probiotics. Most people discover gaps here.
Day 5-7: Schedule doctor appointment if needed. Request vitamin D testing if you have 3+ risk factors.
Week 2: Implementation Phase
If testing shows deficiency:
- Start appropriate supplement at recommended dose
- Set phone reminder to take it daily
- Buy from reputable source with third-party testing
If no testing yet:
- Focus on adding immune-supporting foods
- Try one recipe from this article
- Don’t start supplements “just in case”
Month 1: Monitoring Phase
Start your tracking log. Note:
- Days you remember to take supplements
- How you feel (1-10 scale)
- Any side effects
- Sick days
Be consistent. It takes time to see effects.
Month 3: Evaluation Phase
Review your log. Ask these questions:
Is it working?
- Fewer sick days than usual?
- Better energy or mood?
- Tangible improvements?
Is it sustainable?
- Can you afford to continue?
- Do you remember to take it most days?
- Are side effects manageable?
Is it necessary?
- Could you get same benefits from food?
- Have you improved your foundation (sleep, diet, stress)?
Be honest. If a supplement isn’t clearly helping after 3 months, stop it. Try something else or focus on lifestyle.
Long-Term Strategy
Annual check-in:
- Retest vitamin D levels once yearly (late winter)
- Review your supplement routine
- Adjust based on life changes (new job, moved locations, age)
Stay flexible:
- Your needs change over time
- What works at 30 might not matter at 50
- Pregnancy, illness, stress all shift requirements
Keep learning:
- New research emerges constantly
- Stay open to changing your approach
- Question old habits that aren’t serving you
Conclusion
Let’s recap what research actually shows versus what marketing wants you to believe.
What Works:
- Vitamin D for people who are deficient
- Zinc lozenges within 24 hours of cold symptoms
- Specific probiotic strains for frequent infections
- Vitamin C for people under extreme physical stress
What Doesn’t Work for Most People:
- Vitamin C to prevent colds in the general population
- Echinacea (too inconsistent)
- Generic “immune boost” formulas
- Taking supplements when you’re not deficient
The Real Secret to Strong Immunity:
No supplement replaces these fundamentals:
- Sleep 7-8 hours (lack of sleep cuts immune function in half)
- Eat varied, colorful foods (thousands of beneficial compounds)
- Manage stress (chronic stress suppresses immunity)
- Move regularly (moderate exercise enhances immune surveillance)
- Wash hands often (prevents exposure in the first place)
A study followed 1,000 people through cold season. Those who slept under 6 hours nightly were 4 times more likely to catch a cold. No supplement comes close to that effect.
Smart Supplementation Means:
- Testing to identify actual deficiencies
- Choosing research-backed options
- Using appropriate doses
- Tracking results honestly
- Adjusting based on what works for you
Dumb Supplementation Means:
- Taking everything marketed for immunity
- Never testing to see if you need it
- Hoping supplements replace poor lifestyle habits
- Spending hundreds monthly on unproven products
The supplement industry hit $177 billion in 2023. Much of that money bought false hope, not better health.
Be smarter than the marketing. Use science to guide your choices.
Your Next Step:
Don’t buy another supplement until you:
- Complete the self-assessment
- Fix at least 2 foundation elements (sleep, diet, stress, exercise)
- Get tested if you have risk factors
- Choose one targeted supplement based on actual need
Most people reading this don’t need a cabinet full of bottles. They need better sleep, real food, and maybe one supplement for a specific deficiency.
That’s not exciting. It won’t sell products. But it’s what the research actually shows.
Now you know what works, what doesn’t, and how to make smart choices for your unique situation.
The power is in your hands. Use it wisely.
FAQs
Can I take all these supplements together?
Most combinations are safe. But some interactions exist:
- Zinc blocks copper absorption (take at different times)
- High calcium blocks iron (separate by 2+ hours)
- Probiotics with antibiotics (take probiotics 2-3 hours after antibiotic dose)
Start one supplement at a time. Wait a week. Then add another if needed.
How long before I see results?
Depends on the supplement and your starting point:
- Zinc for colds: Works within 24 hours or not at all
- Vitamin D: 4-12 weeks to see symptom changes, 3 months for levels to normalize
- Probiotics: 2-4 weeks for digestive changes, 4-8 weeks for immune effects
- Vitamin C: Immediate during illness (shortens duration), minimal prevention effect
Are supplements safe during pregnancy?
Some yes, some no, some maybe:
Generally safe:
- Prenatal vitamins with vitamin D
- Probiotics (food sources preferred)
Avoid:
- High-dose vitamin A
- Echinacea
- Elderberry (not enough safety data)
- High-dose vitamin C (over 2000 mg)
Always check with your OB-GYN before taking any supplement during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Do supplements expire?
Yes. Potency decreases over time:
- Most vitamins: Lose 10-20% potency per year after expiration
- Probiotics: Lose effectiveness quickly after expiration
- Elderberry/Herbal: May lose potency or grow mold
Don’t use expired supplements. They won’t harm you, but they won’t help either.
Can children take these supplements?
Some yes, with appropriate dosing:
- Vitamin D: Safe and recommended
- Probiotics (LGG, BB-12): Studied extensively in children
- Zinc: Only during illness, lower doses
- Others: Consult pediatrician first
Never give adult-dose supplements to children.
What’s the difference between synthetic and natural vitamins?
Most vitamins work the same regardless of source:
- Vitamin D3 (from fish oil or lanolin): No difference in effectiveness
- Vitamin C (ascorbic acid): Same whether from oranges or corn
Exceptions:
- Natural vitamin E (d-alpha-tocopherol): Better absorbed than synthetic (dl-alpha-tocopherol)
- Folate from food: Better than synthetic folic acid for some people
For most supplements, synthetic works fine and costs less.
Should I take supplements with or without food?
Depends on the type:
Take with food:
- Fat-soluble vitamins (D, E, K, A): Need dietary fat for absorption
- Zinc: Reduces nausea
- Iron: Better absorbed with vitamin C-rich foods
Take without food:
- Probiotics: Some survive better on empty stomach (30 minutes before meals)
- Zinc lozenges for colds: Need throat contact, not digestion
Doesn’t matter:
- Vitamin C: Water-soluble, absorbs either way
- Most B vitamins: Water-soluble
Can I overdose on these supplements?
Yes, especially fat-soluble vitamins that your body stores:
Toxicity risks:
- Vitamin D: Over 10,000 IU daily long-term can cause calcium buildup
- Zinc: Over 100 mg daily can cause copper deficiency
- Selenium: Over 400 mcg daily causes hair loss, brittle nails
- Vitamin A: Over 10,000 IU daily can damage liver
Water-soluble vitamins (C, B vitamins) are safer. Your body eliminates excess through urine. But mega-doses can still cause issues:
- Vitamin C over 2000 mg: Diarrhea, kidney stones
- Vitamin B6 over 100 mg: Nerve damage
Stick to recommended doses unless supervised by a doctor.
How do I know if a supplement is working?
Track these markers:
For Vitamin D:
- More energy
- Better mood
- Fewer infections
- Blood test shows improved levels
For Probiotics:
- Better digestion
- Fewer colds (track frequency)
- Less severe symptoms when sick
For Zinc (during colds):
- Shorter cold duration (track days)
- Less severe symptoms
Keep a simple log. Note:
- Date started supplement
- Dose taken
- How you feel
- Number of sick days
Compare to previous years. Real patterns take 3-6 months to see.


