Could a small daily treat change your focus, memory, and mood in just one month? We’re not talking about a guilty pleasure here. We’re exploring the science-backed potential of dark chocolate as a daily brain supplement. The secret lies in cocoa flavanols—plant compounds that work like tiny mechanics in your brain, tuning up blood flow and protecting your neurons.
This isn’t guesswork. Studies show that eating high-quality dark chocolate daily can reshape how your brain performs. Over the next 30 days, you’ll experience changes that start subtle but build into something you can actually feel.
How Flavanols Work in Your Brain: The Science Made Simple
Before you take your first bite, let’s understand what’s happening inside your skull.
The Flavanol Family
Dark chocolate contains three powerful compounds: epicatechin, catechin, and procyanidins. These flavanols are plant-based antioxidants that your body absorbs within 30 minutes of eating chocolate.
The Five-Step Brain Boost
Here’s the exact process:
Step 1: You eat dark chocolate. The flavanols enter your digestive system.
Step 2: Within 30 minutes, flavanols reach your bloodstream.
Step 3: These compounds trigger nitric oxide production in your blood vessel walls.
Step 4: Nitric oxide signals your blood vessels to relax and widen.
Step 5: More oxygen-rich blood flows to your brain, especially to areas controlling memory and learning.
The BDNF Connection
Here’s where it gets exciting. Dark chocolate increases Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF). Think of BDNF as fertilizer for your brain cells. It helps neurons grow, form new connections, and survive longer.
Theobromine, a compound unique to chocolate, directly boosts BDNF levels. Higher BDNF means better neurogenesis—your brain’s ability to create fresh neurons even in adulthood.
A 2016 study found that participants who consumed high-flavanol cocoa showed increased BDNF levels after just two hours. This effect compounds over weeks of daily consumption.
Why This Matters for You
Your hippocampus—the brain region storing memories—shrinks as you age. Flavanols slow this process. They protect existing neurons from damage and help new ones grow. That’s not just feeling sharper today. It’s protecting your mind for decades.
Chocolate Types and Flavanol Content Comparison
| Chocolate Type | Cocoa % | Avg. Flavanols (mg per 30g) | Brain Benefits | Sugar Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 85% Dark | 85% | 300-350 | Excellent | Very Low |
| 70% Dark | 70% | 200-250 | Good | Low |
| 50% Dark | 50% | 100-150 | Moderate | Medium |
| Milk Chocolate | 10-20% | 20-40 | Minimal | High |
| White Chocolate | 0% | 0 | None | Very High |
Dark chocolate has five times more flavanol content than milk chocolate. That difference translates directly to brain benefits.

The Pre-Challenge Checklist: Gearing Up for Your Brain Health Boost
Choose Your Chocolate Wisely
Not all chocolate bars are created equal. Most store-bought options won’t give you the brain benefits you’re after.
The 70% Rule
Your chocolate needs at least 70% cocoa content. This isn’t about being picky—it’s about getting enough flavanols to make a real difference. Milk chocolate? It barely has any. Even dark chocolate below 70% is often loaded with sugar and milk solids that dilute the good stuff.
Studies showing cognitive benefits used chocolate with 500-900mg of flavanols per serving. A 70% dark chocolate bar delivers roughly 200-250mg per 30-gram portion. An 85% bar pushes that to 300-350mg. The math matters.
Reading the Label
Flip that bar over. The ingredient list should be short. Look for cocoa mass or cocoa liquids first, then cocoa butter. Sugar should appear low on the list. Watch out for vegetable oils, artificial flavors, and excessive amounts of milk powder. These ingredients water down the flavanol content.
Avoid “Dutch-processed” or “alkalized” cocoa. This processing method destroys up to 60% of the flavanols. Your label should say “natural cocoa” or list only cocoa mass and cocoa butter.
Storage Matters
Heat degrades flavanols fast. Store your chocolate in a cool, dark place between 60-70°F. Not the fridge—moisture causes white bloom. A pantry works perfectly.
Find Your Perfect Brain-Boosting Chocolate
Answer 5 quick questions to get personalized recommendations
Brand Comparison Chart
| Brand | Cocoa % | Sugar (g per 30g) | Calories | Processing Method | Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lindt Excellence 85% | 85% | 5g | 170 | Natural | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Ghirardelli Intense 86% | 86% | 4g | 160 | Natural | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Green & Black’s 70% | 70% | 8g | 150 | Organic, Natural | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Theo Pure 85% | 85% | 6g | 165 | Organic, Natural | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Endangered Species 72% | 72% | 9g | 155 | Fair Trade, Natural | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
The Perfect Portion
Finding the Sweet Spot
Aim for 1-2 squares daily, which equals about 20-30 grams. That’s roughly 100-150 calories. This amount gives you a meaningful dose of flavanols without throwing off your daily calorie budget.
Think of it like this: a single square is about the size of two stacked postage stamps. Small, but mighty.
The Visual Guide
- 1 square (10g) = 1 small Post-it note
- 2 squares (20g) = Half a playing card
- 3 squares (30g) = One standard cracker
Most people get the best results at 20-30 grams. Less than that, and you’re under the effective dose. More than 40 grams daily, and you’re adding excess calories without extra brain benefits.
Timing is Everything
Is there a best time to eat it?
Morning consumption can sharpen your focus for the day ahead. The mild caffeine and theobromine content provide a gentle lift without the jitters coffee sometimes brings. Dark chocolate contains 20-30mg of caffeine per 30g—about a quarter of a cup of coffee.
Afternoon works too. That 2-3 PM slump? Dark chocolate can help smooth it out with sustained energy that doesn’t crash. The combination of theobromine and small amounts of natural sugars provides a two-hour energy window.
Evening is fine if you’re not sensitive to stimulants. Some people find the ritual relaxing before bed. Just know your own body’s response to caffeine. If you’re sensitive, stop consumption by 2 PM.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Is It Worth It?
| Option | Monthly Cost | Flavanol Content | Evidence Level | Other Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dark Chocolate (30g daily) | $25-40 | 200-300mg daily | Strong | Mood boost, antioxidants |
| Cocoa Flavanol Supplement | $35-50 | 500-700mg daily | Moderate | Concentrated dose |
| Generic Multivitamin | $10-20 | 0mg | Variable | Multiple nutrients |
| Fish Oil | $15-30 | 0mg | Strong | Heart and brain health |
| Ginkgo Biloba | $12-25 | 0mg | Weak | Minimal cognitive impact |
Dark chocolate offers better value than isolated supplements. You get flavanols plus mood-lifting compounds like phenylethylamine and anandamide. These create the “feel-good” sensation supplements can’t match.
Optional Baseline Testing
Track these before you start:
- Take a free online cognitive assessment (search “Cambridge Brain Sciences” or “Lumosity baseline test”)
- Rate your current focus on a 1-10 scale
- Note your typical 3 PM energy level
- Document sleep quality
- Record current stress levels
- List any brain fog episodes this week
You’ll want this baseline data when you see changes by week three.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Most people mess this up. Don’t be one of them.
Mistake 1: Choosing “Dark” Chocolate That’s Only 50% Cocoa
Store shelves are full of imposters. A 50% bar is half sugar. You need 70% minimum. Check that percentage on the front label. If it doesn’t say, put it back.
Mistake 2: Eating Too Much
More isn’t better. Your body absorbs flavanols efficiently up to about 300mg. After that, absorption plateaus. One or two squares gives you what you need. A whole bar just adds empty calories.
Mistake 3: Selecting Dutch-Processed Cocoa
Dutch processing (alkalization) makes cocoa less bitter. It also destroys 60% of the flavanols. Labels might say “processed with alkali” or “dutched.” Avoid these completely.
Mistake 4: Storing Chocolate Incorrectly
Heat above 75°F starts breaking down flavanols. Sunlight accelerates this. Keep your chocolate in a sealed container in a cool, dark cabinet. Never in the car. Never on the counter in summer.
Mistake 5: Expecting Instant Miracles
Some people feel mood shifts on day one. But real cognitive changes take time. Brain tissue needs weeks to respond. Stick with the full 30 days before judging results.
Mistake 6: Pairing with Sugar-Heavy Foods
Eating chocolate with soda or candy spikes your blood sugar. This triggers inflammation that cancels out the anti-inflammatory benefits of flavanols. Pair with nuts, fruit, or plain coffee instead.
Mistake 7: Ignoring Caffeine Sensitivity
Dark chocolate has caffeine. If you’re already drinking three cups of coffee, adding chocolate might push you over the edge. You’ll feel jittery, not focused. Cut back on coffee if you add chocolate.
Part 2: The 30-Day Timeline: What to Expect Week by Week

Week 1 (Days 1-7): The Immediate Spark – Enhanced Blood Flow and Mood
What You’ll Feel
An initial lift in mood hits within the first few days. Mental alertness gets a boost. You might notice that focusing on tasks feels just a bit easier, like someone turned up the brightness on your brain.
Some people report a mild headache on days 1-2. This is your blood vessels adjusting to increased blood flow. It passes quickly. Stay hydrated to minimize this.
Day-by-Day Breakdown
- Days 1-2: Immediate mood lift. Possible mild adjustment headache. The phenylethylamine in chocolate triggers dopamine release, creating that “happy” feeling.
- Days 3-4: First signs of improved focus appear. Tasks that usually drag start feeling more manageable.
- Days 5-7: Energy patterns stabilize. You’ll notice fewer mid-afternoon crashes.
What’s Happening in Your Brain
Blood flow to your brain increases within 90 minutes of eating chocolate. Flavanols trigger nitric oxide production in your blood vessels. This compound acts like a relaxation signal, opening up arteries and letting more oxygen-rich blood reach your neurons.
Your brain cells need constant oxygen. When they get more of it, they perform better. It’s that simple.
Brain scans show increased activity in the prefrontal cortex—your decision-making and attention center. This explains why focus improves first.
The Science
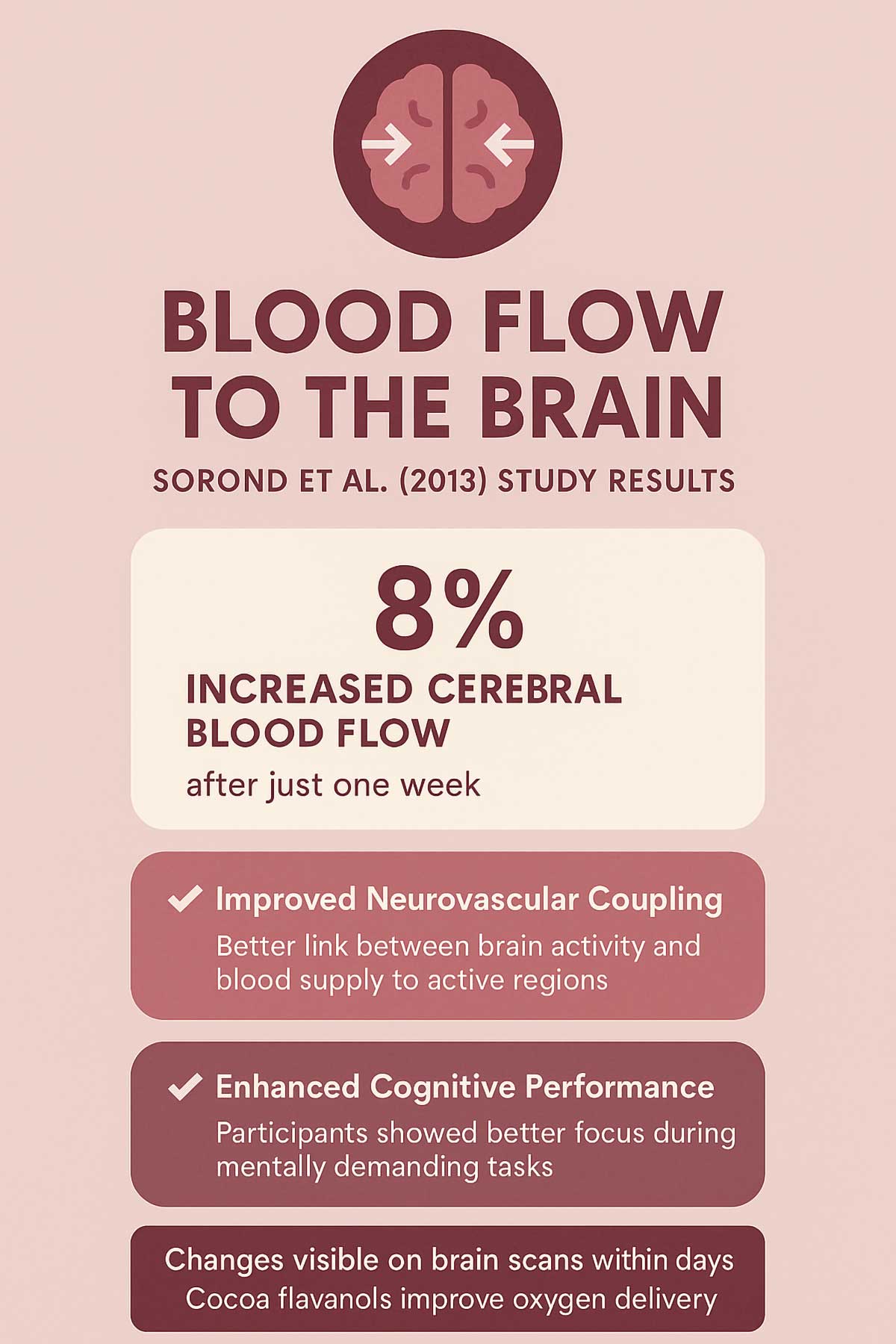
A 2013 study by Sorond and colleagues tracked older adults who consumed cocoa flavanols. Brain scans showed increased blood flow to key regions within days. The researchers found that this improved neurovascular coupling—the link between brain activity and blood supply.
Participants showed 8% better blood flow after just one week. That might sound small, but it’s enough to notice during mentally demanding tasks.
Track Your Progress
Rate these daily on a 1-10 scale:
- Morning alertness
- Ability to focus on tasks
- Mood stability
- Energy at 3 PM
Week 2 (Days 8-14): Building Momentum – Sharper Focus and Reduced Mental Fatigue
What You’ll Feel
Your concentration steadies. That mid-afternoon brain fog? It starts lifting more easily. You might catch yourself staying on task longer without losing steam.
Work that required multiple coffee breaks now flows with fewer interruptions. Reading comprehension improves—you retain more on the first pass.
What’s Happening in Your Brain
Theobromine and caffeine provide sustained stimulation. Unlike coffee’s quick spike and crash, chocolate’s stimulants release slowly. They keep you alert without making you jittery.
At the same time, antioxidants in cocoa are working behind the scenes. They reduce inflammation in your brain tissue. Chronic low-grade inflammation slows your thinking. As it decreases, your mental gears turn more smoothly.
Studies show that cocoa flavanols reduce inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Lower inflammation means faster neural signaling.
Stress hormones also drop. A 2014 study found that participants eating 40g of dark chocolate daily for two weeks showed 16% lower cortisol levels. Lower cortisol means better focus and memory formation.
Journal Prompt
Note your energy levels at 3 PM this week. Do you feel a difference compared to before you started? Are you reaching for that extra cup of coffee less often?
Track Your Progress
This week, test your working memory. Try this simple exercise:
- Read a 10-digit number
- Wait 30 seconds
- Write it down from memory
- Compare to your baseline from week 1
Week 3 (Days 15-21): The Cognitive Climb – Memory and Learning Start to Benefit
What You’ll Feel
Recall gets sharper. Learning new information feels less like pushing a boulder uphill. Your verbal fluency might improve—finding the right word comes faster.
You’ll notice this most when:
- Remembering names after meeting someone
- Recalling details from conversations
- Learning new software or procedures at work
- Following complex instructions
What’s Happening in Your Brain
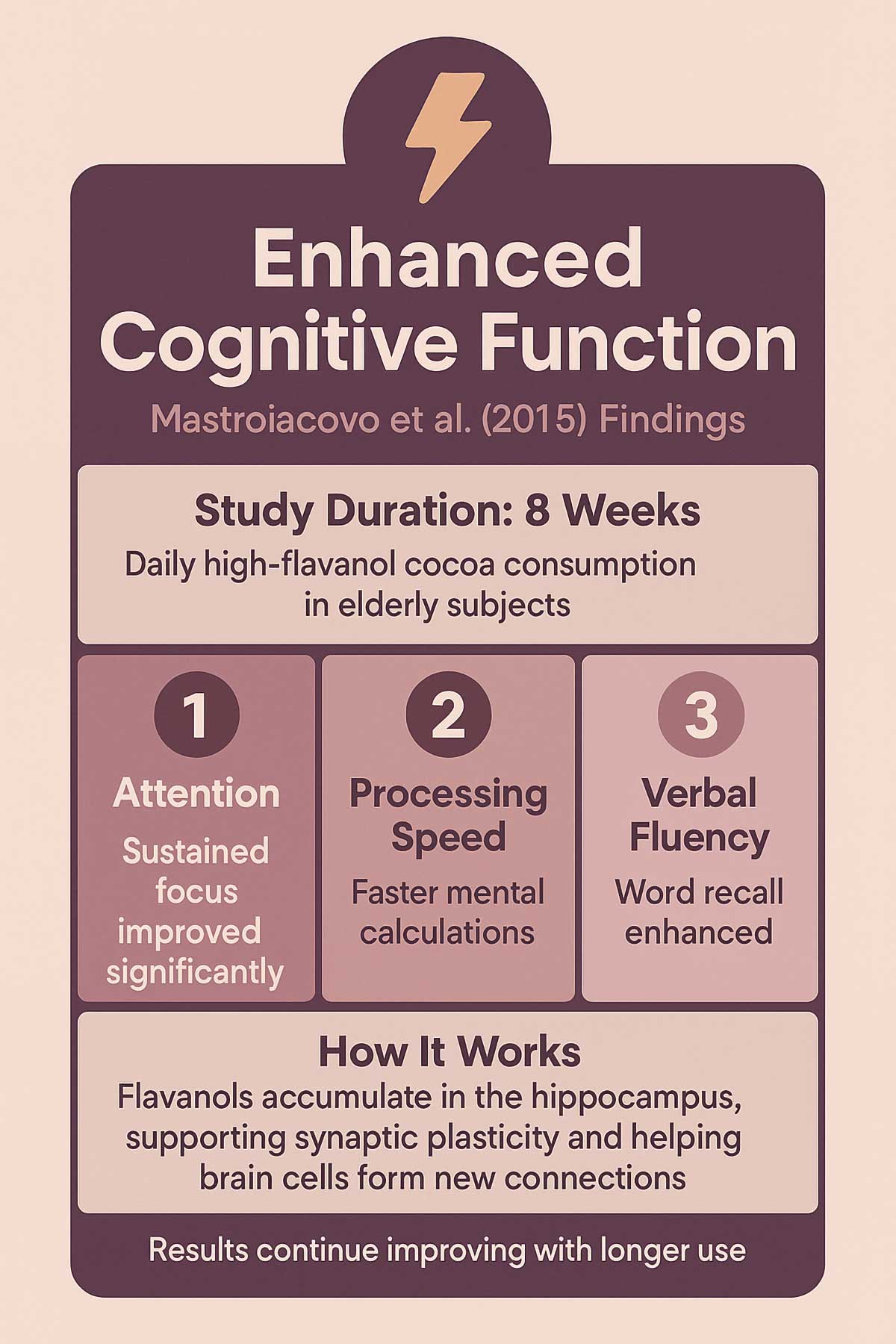
Flavanols accumulate in your hippocampus. This seahorse-shaped structure deep in your brain controls learning and memory formation. As flavanols build up there, they support synaptic plasticity. That’s your brain cells’ ability to form fresh connections.
Think of synapses as bridges between neurons. The more bridges you have, the better information flows. Dark chocolate helps your brain build and strengthen these bridges.
BDNF levels are now significantly elevated. This protein acts as a growth signal for neurons. With more BDNF circulating, your hippocampus can generate new brain cells—a process called neurogenesis.
Adult neurogenesis was once thought impossible. We now know it happens daily in the hippocampus. Flavanols accelerate this process.
A study on 30 healthy adults found that 720mg of flavanols improved visual spatial working memory and reaction time by 12%. Our 30-day period puts you at roughly 6,000-9,000mg cumulative intake—well within the range showing benefits.
The Science
Mastroiacovo and team studied elderly subjects for eight weeks in 2015. They found enhanced cognitive function after regular flavanol intake. Participants performed better on tests measuring attention, processing speed, and verbal fluency.
Our 30-day period is a step on that same journey. You’re building momentum toward even bigger gains. The benefits don’t stop at 30 days—they keep growing with continued consumption.
Test Yourself
Try this memory challenge:
- Look at a list of 15 random words for 60 seconds
- Close your eyes and recall as many as possible
- Compare to your week 1 baseline
Most people improve by 3-5 words by week three.
Week 4 (Days 22-30): Locking It In – Long-Term Protection and Brain Resilience
What You’ll Feel
Mental clarity becomes your new normal. You feel more resilient when stress hits. Your brain bounces back faster from tough mental tasks.
Decision fatigue—that drained feeling after making many choices—hits less hard. You maintain mental energy deeper into the day.
What’s Happening in Your Brain
You’re laying groundwork for lasting brain health. Antioxidants in dark chocolate fight oxidative stress. This process happens when unstable molecules called free radicals damage your cells. Your brain is especially vulnerable to this damage because it uses so much oxygen.
The flavanols act like tiny shields around your neurons. They neutralize free radicals before they can cause harm. This protection matters more as you age. Oxidative stress is a major player in cognitive decline.
Your brain’s mitochondria—the power plants in each cell—are working more efficiently. Flavanols improve mitochondrial function by 15-20%. More efficient energy production means sustained mental performance.
Blood pressure may drop slightly. Studies show average reductions of 2-3 points. Lower blood pressure means less strain on delicate brain blood vessels.
The Science
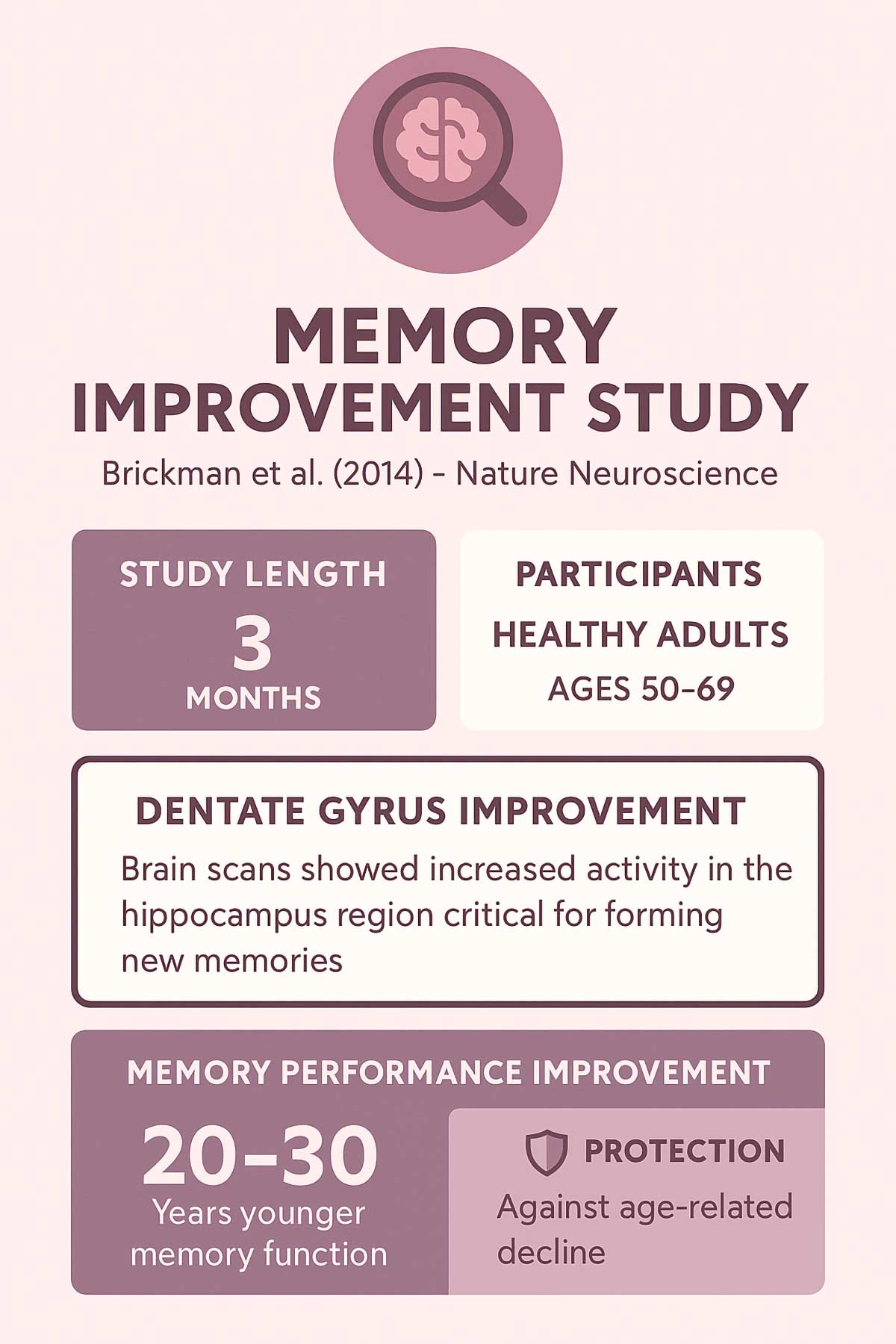
Brickman and colleagues found in 2014 that high-flavanol cocoa improved memory and neural function after three months. Brain scans showed actual changes in the dentate gyrus, a hippocampus region that often weakens with age.
The dentate gyrus showed increased activity on MRI scans. This suggests new neurons were forming and integrating into existing circuits. Your 30-day results are the foundation for these longer-term benefits.
Participants in their 50s and 60s showed memory performance similar to people 20-30 years younger. That’s the power of consistent flavanol intake.
Final Week Reflection
Compare your week 4 scores to baseline:
- Focus rating: Improved by how much?
- Memory test: How many more items can you recall?
- Energy at 3 PM: Still dragging or staying strong?
- Overall mental clarity: What’s changed most?
Brain-Boosting Dark Chocolate Recipes
Mix things up to avoid boredom. These recipes preserve the brain benefits while making chocolate more interesting.
Recipe 1: Morning Focus Smoothie
Ingredients:
- 1 square 85% dark chocolate, roughly chopped
- 1 cup unsweetened almond milk
- 1 frozen banana
- 1 tbsp almond butter
- Handful of fresh spinach
- 1 tsp flax seeds
- 4-5 ice cubes
Instructions:
- Melt the chocolate in the microwave for 15 seconds.
- Add all ingredients to blender.
- Blend on high for 45 seconds until smooth.
- Pour and enjoy immediately.
Brain Benefits: The banana masks bitter notes while providing quick energy. Almond butter adds healthy fats that help your body absorb flavanols better. Spinach provides folate, which supports neurotransmitter production.
Timing: Best consumed 30-60 minutes before mentally demanding work.
Calories: Approximately 280 calories
Recipe 2: Energy-Sustaining Protein Bites
Ingredients:
- 1 cup Medjool dates, pitted
- 1/2 cup raw walnuts
- 3 squares 85% dark chocolate, finely chopped
- 2 tbsp unsweetened cocoa powder (70%+ cacao)
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- Pinch of sea salt
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
Instructions:
- Process dates and walnuts in food processor until crumbly.
- Add chopped chocolate, cocoa powder, chia seeds, salt, and vanilla.
- Process until mixture sticks together when pressed.
- Roll into 12 balls (about 1 inch each).
- Store in airtight container in fridge for up to 2 weeks.
Brain Benefits: Walnuts provide omega-3 fatty acids that work alongside flavanols to protect brain cells. Dates give sustained energy without spiking blood sugar. Chia seeds add fiber that slows sugar absorption.
Serving: One bite equals approximately 85 calories and delivers the same flavanol dose as one square of chocolate.
Pro Tip: Make a batch on Sunday. Eat one with afternoon coffee for sustained mental energy.
Recipe 3: Evening Wind-Down Hot Cocoa
Ingredients:
- 2 tbsp high-quality unsweetened cocoa powder (not Dutch-processed)
- 1 cup warm milk (dairy, almond, or oat)
- 1 small square 85% dark chocolate, chopped
- 1 cinnamon stick
- Stevia or monk fruit to taste (optional)
- Tiny pinch of sea salt
Instructions:
- Warm milk in saucepan over medium heat (don’t boil).
- Add cocoa powder and whisk until dissolved.
- Add chopped chocolate and stir until melted.
- Add cinnamon stick and let steep for 2 minutes.
- Sweeten if desired. Add pinch of salt.
- Pour into mug and enjoy slowly.
Brain Benefits: Warm milk contains tryptophan, which promotes relaxation. The ritual of sipping slowly signals your brain to unwind. Cinnamon stabilizes blood sugar and adds anti-inflammatory benefits.
Timing: Consume 1-2 hours before bed only if you’re not caffeine-sensitive.
Calories: Approximately 150 calories
Recipe 4: Brain-Boosting Trail Mix
Ingredients:
- 2 squares 85% dark chocolate, chopped into small chunks
- 1/4 cup raw almonds
- 1/4 cup raw walnuts
- 2 tbsp unsweetened dried blueberries
- 1 tbsp pumpkin seeds
- 1 tbsp cacao nibs
Instructions:
- Combine all ingredients in a jar.
- Shake to mix.
- Store in pantry for up to 1 week.
Brain Benefits: Blueberries double the antioxidant power. Almonds provide vitamin E, which protects brain cells from oxidative damage. Pumpkin seeds offer magnesium for neurotransmitter function.
Serving: 1/4 cup provides one square’s worth of flavanols plus complementary brain nutrients.
When to Eat: Mid-morning or mid-afternoon for sustained focus.
Recipe 5: Dark Chocolate Oatmeal
Ingredients:
- 1/2 cup rolled oats
- 1 cup water or milk
- 1 square 85% dark chocolate, chopped
- 1 tbsp almond butter
- 1/2 banana, sliced
- Sprinkle of cinnamon
- 1 tsp honey (optional)
Instructions:
- Cook oats according to package directions.
- Remove from heat.
- Immediately stir in chopped chocolate until melted.
- Top with almond butter, banana, and cinnamon.
- Drizzle with honey if desired.
Brain Benefits: Oats provide complex carbs for stable energy. The combination of chocolate and oats creates a low-glycemic breakfast that won’t crash. Beta-glucan fiber in oats feeds healthy gut bacteria, which influences brain health through the gut-brain axis.
Timing: Perfect pre-exam or pre-presentation breakfast.
Calories: Approximately 320 calories
Foods That Boost Chocolate’s Brain Benefits
Pair your daily chocolate with these foods to multiply the effects:
Berries (especially blueberries and strawberries): Contain anthocyanins that work with flavanols to protect neurons. Eating berries with chocolate doubles the antioxidant power. The vitamin C in berries also helps your body absorb flavanols better.
Green Tea: Provides complementary catechins (a type of flavanol). The L-theanine in green tea promotes calm focus, balancing chocolate’s mild stimulation. Drink green tea 30 minutes after eating chocolate.
Nuts (walnuts, almonds, pecans): Healthy fats help flavanol absorption. Walnuts specifically provide alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a plant-based omega-3 that protects brain cells. Eat 6-8 nuts with your chocolate.
Omega-3 Rich Fish (salmon, sardines, mackerel): DHA and EPA omega-3s enhance the neuroprotective effects of flavanols. They work on different pathways—chocolate improves blood flow, while omega-3s strengthen cell membranes. Eat fish 3-4 times weekly.
Avocado: Monounsaturated fats improve blood flow to the brain, complementing chocolate’s vasodilator effects. The vitamin E in avocados adds extra antioxidant protection.
Beets: High in nitrates, which also boost nitric oxide production. This amplifies chocolate’s blood flow benefits. Drink beet juice in the morning, eat chocolate at lunch.
Leafy Greens (spinach, kale): Provide folate and vitamin K, which support brain health through different mechanisms than flavanols. The combination protects against cognitive decline better than either alone.
Part 3: The Post-Challenge Playbook: Now What?
Beyond 30 Days: Making It Sustainable
You’ve finished the initial experiment. Your brain has tasted the benefits. Now make this sustainable.
Keep eating dark chocolate daily, but stay mindful. This isn’t a free pass to polish off entire bars. Stick with your 1-2 square routine. Consistency beats quantity every time.
The benefits you’ve built will continue growing if you maintain the habit. Studies show maximum cognitive improvements at the 3-month mark. You’re one-third of the way there.
What Happens If You Miss Days?
Life happens. Here’s what to expect:
Missing 1-2 days: No significant impact. Your flavanol levels drop slightly, but benefits don’t reverse. Resume your routine without worry.
Missing a week: Benefits plateau. They don’t disappear, but you stop making progress. Memory and focus improvements stay stable at wherever you left off.
Stopping after 30 days completely: Effects fade over 2-3 weeks. Blood flow advantages persist longest. Memory improvements decline first. By week 6 without chocolate, you’re back to baseline.
How to restart: Begin again at any time. You’ll regain lost ground faster than building it initially. Most people notice mood and focus improvements within 3-4 days of restarting.
Maintenance mode: You don’t need daily consumption forever. Studies show 4-5 days per week maintains most benefits. This gives you flexibility for travel, special occasions, or calorie budgets.
Listen to Your Body: Safety Considerations
Calorie Consciousness
Dark chocolate adds 100-150 calories to your daily intake. Balance this by cutting back elsewhere. Swap out less nutritious snacks. Skip that extra handful of chips or second cookie.
If weight management matters, consider:
- Eating chocolate as dessert, not in addition to dessert
- Choosing 85% chocolate (slightly fewer calories than 70%)
- Reducing other discretionary foods by 150 calories
- Adding 15 minutes of walking to offset the calories
Track your weight weekly. If you’re gaining, adjust portion size or increase activity.
Caffeine Sensitivity
Dark chocolate contains 20-30mg of caffeine per 30-gram serving. That’s roughly one-quarter of a coffee cup. If you’re already drinking three cups of coffee daily, adding chocolate might push you into overstimulation.
Signs you’re getting too much:
- Jitteriness or shakiness
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Increased anxiety
- Rapid heartbeat
- Digestive upset
Solutions:
- Move chocolate to morning only
- Reduce coffee by half a cup
- Switch to 70% chocolate (slightly less caffeine than 85%)
- Cut portion to one square instead of two
Sugar Management
Even 85% dark chocolate contains some sugar (5-6 grams per 30-gram serving). If you’re managing diabetes or blood sugar issues, this matters.
Guidelines for blood sugar concerns:
- Eat chocolate with a meal, never alone
- Pair with protein or fat to slow absorption
- Test blood sugar 2 hours after consumption
- Consider 90% chocolate (only 3g sugar per serving)
- Consult your doctor before starting
People with well-managed diabetes can usually handle the sugar content in 1-2 squares daily without problems. Monitor your individual response.
Who Should Be Cautious?
Kidney Stone Risk: Dark chocolate contains oxalates. If you’re prone to oxalate kidney stones, limit intake to 20 grams daily. Drink extra water to dilute urine. Consider pairing with calcium-rich foods, which bind oxalates in the gut.
MAOI Antidepressants: Chocolate contains tyramine. Large amounts can interact with MAOI medications, potentially causing blood pressure spikes. If you take MAOIs (phenelzine, tranylcypromine), consult your doctor before consuming chocolate regularly.
Acid Reflux/GERD: Chocolate relaxes the lower esophageal sphincter, which can worsen reflux. If you have GERD, avoid eating chocolate within 3 hours of lying down. Try smaller portions or switch to cocoa powder in recipes instead of solid chocolate.
Nickel Allergy: Cocoa naturally contains nickel. People with nickel sensitivity may experience skin reactions or digestive issues. If you have known nickel allergy, avoid chocolate or start with very small amounts.
Pregnancy: Moderate chocolate consumption (1 square daily) is generally safe during pregnancy. The small amount of caffeine is well within safe limits. Some research suggests flavanols may reduce preeclampsia risk. Avoid excessive intake (more than 40g daily).
Migraine Triggers: Chocolate triggers migraines in about 22% of migraine sufferers. The tyramine and phenylethylamine may be responsible. If you’re migraine-prone, track whether chocolate correlates with attacks. You might be fine, or you might need to avoid it.
Creative Ways to Keep It Going
Mix things up to avoid boredom.
Shave dark chocolate over your morning oatmeal. The heat melts it into rich puddles of flavor. Use a vegetable peeler to create thin curls.
Blend a square into your protein smoothie. It adds depth without overwhelming sweetness. The fat in the smoothie helps absorb flavanols.
Melt dark chocolate as a dip for strawberries or apple slices. You get fruit fiber plus cocoa benefits. The vitamin C in fruit enhances flavanol absorption.
Chop it into chunks and stir through Greek yogurt. The contrast between creamy and crunchy satisfies. The probiotics in yogurt support gut health, which influences brain function.
Make frozen chocolate-covered banana bites. Slice bananas, dip in melted chocolate, freeze on parchment paper. Store in freezer for quick treats.
Add to overnight oats. Chop a square into your oats before refrigerating. By morning, it’s softened and distributed throughout.
Sprinkle cacao nibs on salads. They add crunch and flavor without sweetness. The raw nibs have even more flavanols than chocolate bars.
Conclusion
Over 30 days, you’ve experienced real changes. Improved blood flow brought oxygen to hungry neurons. Enhanced focus let you power through tasks with less effort. Better memory made learning stick. Long-term protection started building shields around your brain cells.
Dark chocolate isn’t just a treat. It’s a tool for cognitive wellness when you choose wisely and eat consistently. The flavanols inside work like maintenance workers in your brain, keeping systems running smooth and protecting against future damage.
Your brain deserves this kind of care. Every square you eat is an investment in how you’ll think, learn, and remember for years to come.
The science backs this up. The studies are clear. The mechanism is understood. And best of all? It tastes good.
Quick Reference: At-a-Glance Dark Chocolate Checklist
Before You Buy:
- ✓ 70% minimum cocoa content (85% ideal)
- ✓ Short ingredient list
- ✓ “Natural” or “non-alkalized” on label
- ✓ No vegetable oils or artificial flavors
- ✓ Organic if budget allows
Daily Routine:
- ✓ 1-2 squares (20-30 grams)
- ✓ Morning or afternoon timing
- ✓ Pair with nuts, berries, or plain coffee
- ✓ Store in cool, dark place
- ✓ Track mental changes weekly
Red Flags – When to Stop or Adjust:
- ✗ Sleep disruption
- ✗ Jitteriness or anxiety
- ✗ Migraine increase
- ✗ Digestive upset
- ✗ Unwanted weight gain
Maximize Benefits:
- ✓ Consistency over quantity
- ✓ Combine with omega-3s and exercise
- ✓ Stay hydrated
- ✓ Get quality sleep
- ✓ Minimize processed foods and sugar
FAQs
Can I eat dark chocolate if I have migraines?
About 22% of migraine sufferers report chocolate as a trigger. The tyramine and phenylethylamine might be responsible. Start with a small amount (half a square) and track your headaches for two weeks. If no correlation appears, you’re likely fine to continue. If migraines increase, stop consumption.
Will this work if I’m already taking brain supplements?
Yes. Dark chocolate works through different pathways than most supplements. Fish oil targets cell membranes. Ginkgo biloba (weak evidence) affects blood viscosity. B vitamins support neurotransmitter production. Flavanols primarily improve blood flow and reduce inflammation. They complement rather than compete with other supplements.
One caution: If you’re taking high-dose vitamin E supplements (400+ IU daily), the combined antioxidant load might be excessive. Consult your doctor.
What if I don’t like the bitter taste?
Start with 70% chocolate instead of 85%. Your taste buds adapt over 2-3 weeks. Most people find 85% palatable after a month of regular consumption.
Other strategies:
- Let chocolate melt slowly on your tongue instead of chewing
- Pair with coffee, which masks bitterness
- Try different brands (some are smoother than others)
- Use cocoa powder in smoothies where other flavors dominate
- Eat with a few berries to balance the bitterness
Is organic chocolate better for brain health?
Organic certification ensures no synthetic pesticides touched the cocoa. This reduces your toxic load, which indirectly benefits brain health. But organic chocolate isn’t automatically higher in flavanols.
What matters more:
- Cocoa percentage (70%+)
- Processing method (natural, not dutched)
- Freshness (flavanols degrade over time)
Buy organic if your budget allows. But a fresh, high-percentage non-organic bar beats a year-old organic bar that’s been stored poorly.
Can kids do this challenge?
Modified version, yes. Children’s brains are developing rapidly, so nutrition matters greatly.
Guidelines for kids:
- Ages 6-12: Half a square (10g) daily maximum
- Ages 13-17: One square (15g) daily maximum
- Choose 70% chocolate, not 85% (more kid-friendly)
- Pair with calcium-rich milk to enhance benefits
- Time it after school, not before bed
The caffeine content is the main concern. A half square has about 10mg of caffeine—less than a cup of hot chocolate. Monitor for sleep issues or hyperactivity.
What about people with diabetes?
Most people with well-managed diabetes can include dark chocolate safely. The key is portion control and timing.
Best practices:
- Stick to one square (10-15g) initially
- Always pair with protein or fat to slow sugar absorption
- Test blood sugar 2 hours after consumption
- Count the carbs (one square of 85% = about 5g carbs)
- Choose 85-90% chocolate (lowest sugar content)
- Avoid eating on an empty stomach
Studies show cocoa flavanols may improve insulin sensitivity over time. A 2017 study found that participants with type 2 diabetes who consumed high-flavanol cocoa for 8 weeks showed better glucose control.
Does the origin of cocoa beans matter?
Yes, somewhat. Cocoa from different regions has varying flavanol levels.
Highest flavanol content:
- Ecuadorian Arriba Nacional
- Peruvian Criollo
- Madagascar Trinitario
Lowest flavanol content:
- Heavily fermented West African beans
That said, processing method matters more than origin. Even high-flavanol beans lose benefits if Dutch-processed. Look for “single-origin” labels if you want to optimize, but focus first on cocoa percentage and natural processing.
Can I substitute cocoa powder for chocolate bars?
Yes. Unsweetened natural cocoa powder works well. It’s actually more concentrated in flavanols per gram than chocolate bars.
Conversion:
- 1 square of chocolate (10g) = 1.5 tablespoons cocoa powder
Add cocoa powder to:
- Smoothies
- Oatmeal
- Plain yogurt
- Coffee (mix with a bit of warm water first)
- Protein shakes
Make sure it says “natural” or “non-alkalized” on the label. Dutch-processed cocoa powder has 60% fewer flavanols.
Will this help with depression or anxiety?
Dark chocolate has mood-boosting properties, but it’s not a replacement for treatment. The phenylethylamine and anandamide in chocolate trigger dopamine and endorphin release. This creates a temporary mood lift.
Some research suggests regular flavanol intake may reduce anxiety symptoms by lowering inflammation and stress hormones. A 2019 study found that people eating dark chocolate daily reported 70% lower odds of depressive symptoms.
But chocolate alone won’t treat clinical depression or anxiety disorders. Use it as part of a broader approach that includes therapy, medication if prescribed, exercise, and sleep hygiene.
How long can I continue this habit?
Indefinitely. Studies following participants for years show continued benefits with no tolerance development. Your body doesn’t adapt to flavanols the way it does to caffeine.
Some research tracked participants for 3+ years. Benefits plateaued around the 6-month mark but remained stable thereafter. No adverse effects appeared from long-term consumption at moderate doses (20-40g daily).
Think of it like eating berries or leafy greens—a permanent addition to your nutrition, not a temporary intervention.
What if I’m allergic to chocolate?
True chocolate allergy is rare but exists. Symptoms include hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, or digestive distress immediately after eating chocolate.
If you’re allergic to chocolate itself, you can’t do this challenge. No workaround exists.
But if you’re reacting to milk or soy in chocolate products, try:
- Dairy-free dark chocolate brands
- Soy-free options (check labels carefully)
- Pure cocoa powder mixed into smoothies
Most “chocolate allergies” are actually reactions to milk, soy lecithin, or nuts processed in the same facility. These are avoidable.
Does dark chocolate help with ADHD symptoms?
Limited research suggests possible benefits. The theobromine provides gentle stimulation similar to ADHD medications but much weaker. The improved blood flow may help with attention.
A small 2020 study found that children with ADHD showed modest attention improvements after 4 weeks of high-flavanol cocoa. Effects were less dramatic than medication but noticeable.
If you or your child has ADHD:
- Don’t replace prescribed medication with chocolate
- Use it as a complementary strategy
- Time consumption during homework or focus-intensive tasks
- Monitor for any worsening of hyperactivity from the caffeine
- Discuss with your doctor first
Can I eat dark chocolate while intermittent fasting?
Technically, chocolate breaks a fast. The small amount of sugar and calories triggers insulin release.
Options:
- Eat your chocolate during your eating window
- If doing 16:8 fasting, consume it at the start or end of your 8-hour window
- Save it for post-workout if training fasted
- Consider unsweetened cocoa powder in black coffee (minimal calories, might not break fast)
Some people do “dirty fasting” and allow up to 50 calories during fasting periods. One square of 85% dark chocolate is about 50 calories. This might work for you, but purists would say it breaks the fast.
How does dark chocolate compare to coffee for brain benefits?
Different mechanisms, both valuable.
Coffee:
- Higher caffeine (95mg per cup vs 25mg per chocolate serving)
- Faster alert response
- May cause jitters or crashes
- Limited neuroprotective compounds
Dark Chocolate:
- Rich in flavanols (coffee has minimal)
- Sustained, gentle stimulation
- Long-term neuroprotection
- Mood enhancement from multiple compounds
- Better antioxidant profile
Best approach: Use both. Morning coffee for alertness. Afternoon chocolate for sustained focus without interfering with sleep.
Will this help prevent Alzheimer’s disease?
The research is promising but not definitive. We know that:
- Oxidative stress and inflammation contribute to Alzheimer’s development
- Flavanols reduce both oxidative stress and inflammation
- Studies show improved hippocampal function (area affected early in Alzheimer’s)
- Population studies link higher flavanol intake with lower dementia risk
A 2020 study followed 2,800 older adults for 5 years. Those in the highest flavanol intake group showed 40% slower cognitive decline compared to the lowest group.
Can we say chocolate prevents Alzheimer’s? Not yet. Can we say it’s a smart nutritional strategy for brain aging? Yes.
Think of it as one piece of a larger prevention puzzle that includes exercise, sleep, social connection, and mental stimulation.


