Testosterone plays a vital role in muscle growth, energy levels, and overall vitality. When levels dip, men often notice fatigue, decreased strength, and a lack of motivation. It’s no surprise that the supplement industry has exploded with products claiming to naturally boost this crucial hormone.
But here’s the problem: most advice lumps all supplements together without telling you which ones actually have solid science behind them. We’re taking a different approach. This article ranks 7 popular testosterone supplements based on the quality of clinical research, from robust human trials to those that simply don’t deliver. We’ll also tell you exactly who each supplement might help and who’s just wasting their money.
Before we continue, let’s be clear: no pill can replace the basics. Sleep, strength training, stress management, and proper nutrition form the foundation of healthy testosterone. Some supplements can offer targeted support, but only when used correctly and by the right people.
Should You Test Your Testosterone First?
Before spending money on supplements, knowing your baseline helps. Here’s what you need to know about getting tested.
What to Test:
- Total testosterone (the big picture)
- Free testosterone (what’s actually available to your tissues)
- SHBG (sex hormone-binding globulin, which binds testosterone)
- Vitamin D, zinc, and magnesium levels if you’re considering those supplements
When to Test: Morning between 7-10 AM. Testosterone peaks early in the day, so afternoon tests can give misleadingly low readings. Avoid testing after poor sleep or intense training, as both temporarily suppress levels.
Normal Ranges:
- Total T: 300-1,000 ng/dL (varies by lab and age)
- Free T: 50-200 pg/mL
- Below 300 ng/dL typically warrants medical evaluation
Where to Test: Your doctor can order comprehensive hormone panels. Direct-to-consumer labs like Quest and LabCorp offer testosterone testing for $50-150 without a doctor’s visit. This baseline data tells you whether you even need supplements or if something else is going on.
Find Your Perfect Testosterone Supplement
Answer 8 quick questions to get personalized recommendations
Quick Reference: Testosterone Supplement Comparison
| Supplement | Evidence Quality | Typical Dose | Best For | Time to Results | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ashwagandha | Strong (RCTs) | 300-600 mg/day | Stressed/active men | 8-12 weeks | $-$$ |
| Tongkat Ali | Strong (Meta-analyses) | 200-400 mg/day | Men with low-T | 4-12 weeks | $$-$$$ |
| Fenugreek | Moderate (Meta-analysis) | 500-600 mg/day | Libido + T support | 8-12 weeks | $ |
| Zinc | Strong (for deficient) | 15-30 mg/day | Zinc-deficient only | 4-8 weeks | $ |
| Vitamin D | Strong (for deficient) | 2000-4000 IU/day | Deficient individuals | 12+ weeks | $ |
| Magnesium | Moderate (for active) | 200-400 mg/day | Athletes | 4-8 weeks | $ |
| D-Aspartic Acid | Weak (no effect) | N/A | No one | N/A | $$ |
Part 1: The Heavy Hitters — Strongest Scientific Backing
These three supplements have the most consistent positive results in human clinical trials. They won’t work miracles, but they can provide modest support for specific groups of men.
1. Ashwagandha: The Stress-Busting T-Booster
What Researchers Found: Ashwagandha has shown real promise in multiple studies. Men under high stress or engaged in resistance training saw testosterone levels rise by about 10-15%. That’s not a dramatic jump, but it’s meaningful. The herb also improved strength markers and DHEA-S levels, a precursor hormone to testosterone.
The studies focused on men dealing with chronic stress or those actively lifting weights. The magic seems to happen when your body is under physical or mental strain. Ashwagandha appears to help your system recover and maintain better hormonal balance.
A 2019 study in the American Journal of Men’s Health tracked 57 men taking 600 mg of ashwagandha daily for eight weeks. The ashwagandha group showed a 14.7% increase in testosterone compared to just 1.5% in the placebo group. They also reported better sleep quality and reduced anxiety scores. The researchers noted that stress reduction might be the mechanism driving the testosterone boost.
Another study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition examined resistance-trained men. After eight weeks of supplementation with 300 mg of ashwagandha twice daily, participants showed significant improvements in muscle strength, muscle size, and testosterone recovery after workouts. The average testosterone increase was 96.2 ng/dL compared to just 18 ng/dL in the placebo group.
Who It’s Best For: Men experiencing high stress levels or those who train regularly. If you’re constantly juggling work deadlines while hitting the gym, this might be your supplement.
The Verdict: ✅ Helps Modestly
Think of ashwagandha as a support system, not a quick fix. It won’t transform your hormone levels overnight, but over 8-12 weeks, it can help stressed or active men maintain healthier testosterone production.
How to Take It:
- Dose: 300-600 mg of standardized extract (containing 5% withanolides or KSM-66 extract) daily
- Timing: Take with meals to reduce stomach upset. Split into morning and evening doses if taking 600 mg
- Form: Capsules work best for consistent dosing. Powder can be mixed into smoothies but tastes bitter
- Cycle: 8-12 weeks on, 2-4 weeks off to prevent your body from adapting
- Interactions: May increase thyroid hormone levels. Consult your doctor if you’re on thyroid medication or have hyperthyroidism

2. Tongkat Ali: The Support for Low-T Men
What Researchers Found: This Southeast Asian herb has impressive data backing it up. Recent analyses of multiple studies show significant increases in total testosterone, especially in men starting with low baseline levels or experiencing fatigue symptoms.
What makes tongkat ali stand out is consistency. Study after study shows similar results, which gives researchers confidence in its effects. The improvements are most dramatic in men who already have low testosterone or feel the symptoms of declining levels.
A 2022 meta-analysis published in Nutrients examined data from multiple clinical trials involving over 1,000 men. Researchers found that tongkat ali supplementation led to statistically significant increases in total testosterone, particularly in men with late-onset hypogonadism or those experiencing stress-related fatigue. The average increase ranged from 15-20% in men with low baseline levels.
Who It’s Best For: Men with clinically low testosterone or those dealing with significant fatigue. If you’ve had blood work showing low-normal or deficient testosterone, tongkat ali deserves consideration.
The Verdict: ✅ Supports Low-T Men
This supplement shines when you need it most. Men with healthy testosterone levels won’t see much benefit, but those struggling with low levels might find real relief. It’s targeted support for a specific problem.
How to Take It:
- Dose: 200-400 mg of standardized extract (100:1 or 200:1 extract ratio) daily
- Timing: Take in the morning with breakfast for energy support throughout the day
- Form: Capsules containing standardized extracts are most reliable
- Cycle: Can be taken continuously, but some users prefer 5 days on, 2 days off
- Interactions: May interact with blood pressure medications. Monitor blood sugar if diabetic, as it may lower glucose levels

3. Fenugreek: The Libido and T-Enhancer
What Researchers Found: A 2020 analysis combining multiple studies confirmed that fenugreek can moderately increase total testosterone. But here’s the catch: quality matters. The research shows that standardized extracts at doses above 500 mg per day produce the best results.
Fenugreek also appears to boost libido alongside testosterone. Men reported improved sexual function and desire in addition to hormonal changes. This dual benefit sets it apart from some other supplements.
The meta-analysis published in Phytotherapy Research pooled data from several randomized controlled trials. Men taking fenugreek extracts experienced an average testosterone increase of 12.26% along with improvements in sexual function scores. The researchers emphasized that results varied significantly based on extract quality and dosage.
A more recent 2024 study followed men taking 500 mg of a specific fenugreek extract daily. After 12 weeks, participants showed not only increased testosterone but also reduced waist size and improved metabolic markers. This suggests fenugreek might support overall male health beyond just hormones.
Who It’s Best For: Men looking for a moderate boost in both testosterone and sexual health. If declining libido concerns you as much as energy levels, fenugreek addresses both issues.
The Verdict: ✅ Helps Modestly
Fenugreek won’t double your testosterone, but it can provide a noticeable lift when taken consistently. Make sure you’re getting a quality extract at the right dose, though. Cheaper products often don’t contain enough active compounds to make a difference.
How to Take It:
- Dose: 500-600 mg of standardized extract (with furostanolic saponins) daily
- Timing: Take with your largest meal of the day
- Form: Capsules or tablets. Avoid whole fenugreek seeds, which aren’t concentrated enough
- Cycle: Can be taken continuously for 12+ weeks
- Interactions: May affect blood sugar levels. Diabetics should monitor glucose. Can cause a maple syrup smell in sweat and urine (harmless but noticeable)

Part 2: The Conditionals — Effective Only If You’re Deficient
Here’s where things get interesting. These three nutrients can absolutely boost testosterone, but only if you’re running low on them to begin with. If your levels are normal, taking more won’t help.
4. Zinc: The Foundational Mineral
What Researchers Found: The science on zinc is crystal clear. If you’re deficient, supplementing will restore your testosterone levels. Studies show dramatic improvements in men with low zinc status. But here’s the kicker: if your zinc levels are already adequate, extra supplementation does nothing for testosterone.
Zinc deficiency is more common than you might think. Vegetarians, heavy exercisers who lose minerals through sweat, and older adults are at higher risk. But taking zinc blindly without knowing your status is a gamble.
The landmark study by Prasad and colleagues in 1996 tracked men with marginal zinc deficiency. After six months of zinc supplementation, testosterone levels nearly doubled from an average of 8.3 nmol/L to 16.0 nmol/L. The catch? All participants started with documented zinc deficiency. Follow-up studies in zinc-replete men showed no testosterone benefits.
Who It’s Best For: Individuals with a diagnosed or suspected zinc deficiency. Before buying zinc supplements, consider getting tested or honestly assess your diet and lifestyle. Signs of deficiency include frequent colds, slow wound healing, hair loss, and decreased sense of taste.
The Verdict: ⚖️ Conditional
“Zinc is essential for testosterone production, but more isn’t better. It’s like filling a gas tank—once it’s full, adding more just spills over.”
Get your levels checked or pay attention to signs of deficiency. Vegetarians and athletes are most likely to benefit.
How to Take It:
- Dose: 15-30 mg daily. Don’t exceed 40 mg, as higher doses can impair copper absorption and immune function
- Timing: Take with food to prevent nausea. Avoid taking with calcium or iron supplements, which compete for absorption
- Form: Zinc picolinate or zinc glycinate absorb better than zinc oxide
- Cycle: Can be taken continuously if deficient. Reassess after 3-6 months with blood work
- Interactions: Reduces copper absorption. Take copper (1-2 mg) if supplementing zinc long-term

5. Vitamin D: The Sunshine Hormone
What Researchers Found: Vitamin D research shows a similar pattern to zinc. Men who are deficient see real benefits from supplementation. Their testosterone levels rise and stabilize. Men with sufficient vitamin D levels? No change.
The challenge is that vitamin D deficiency is extremely common, especially in northern climates or among people who work indoors. If you rarely see sunshine or live above the 37th parallel, there’s a good chance you’re low. But again, testing helps you know for sure.
A 2024 meta-analysis published in Diseases reviewed multiple studies on vitamin D and testosterone. The researchers found that supplementation only benefited men with baseline vitamin D levels below 20 ng/mL. For these deficient men, bringing levels up to 30-40 ng/mL corresponded with testosterone increases of 20-25%. Men who started with adequate vitamin D saw no hormonal changes.
Who It’s Best For: Men deficient in vitamin D, particularly during winter months or those with limited sun exposure. If you live in a place with long, dark winters, vitamin D supplementation makes sense.
The Verdict: ⚖️ Inconsistent
The inconsistency comes from the population studied, not the vitamin itself. Vitamin D works when you need it. The problem is that blanket recommendations don’t account for individual status. A blood test removes the guesswork.
How to Take It:
- Dose: 2,000-4,000 IU daily for maintenance. Higher doses (5,000-10,000 IU) may be needed initially if severely deficient
- Timing: Take with a fat-containing meal. Vitamin D is fat-soluble and absorbs poorly without dietary fat
- Form: Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is more effective than D2
- Cycle: Take continuously, especially during winter months
- Interactions: Safe with most medications. Retest blood levels after 3 months to ensure you’re in the optimal range (40-60 ng/mL)

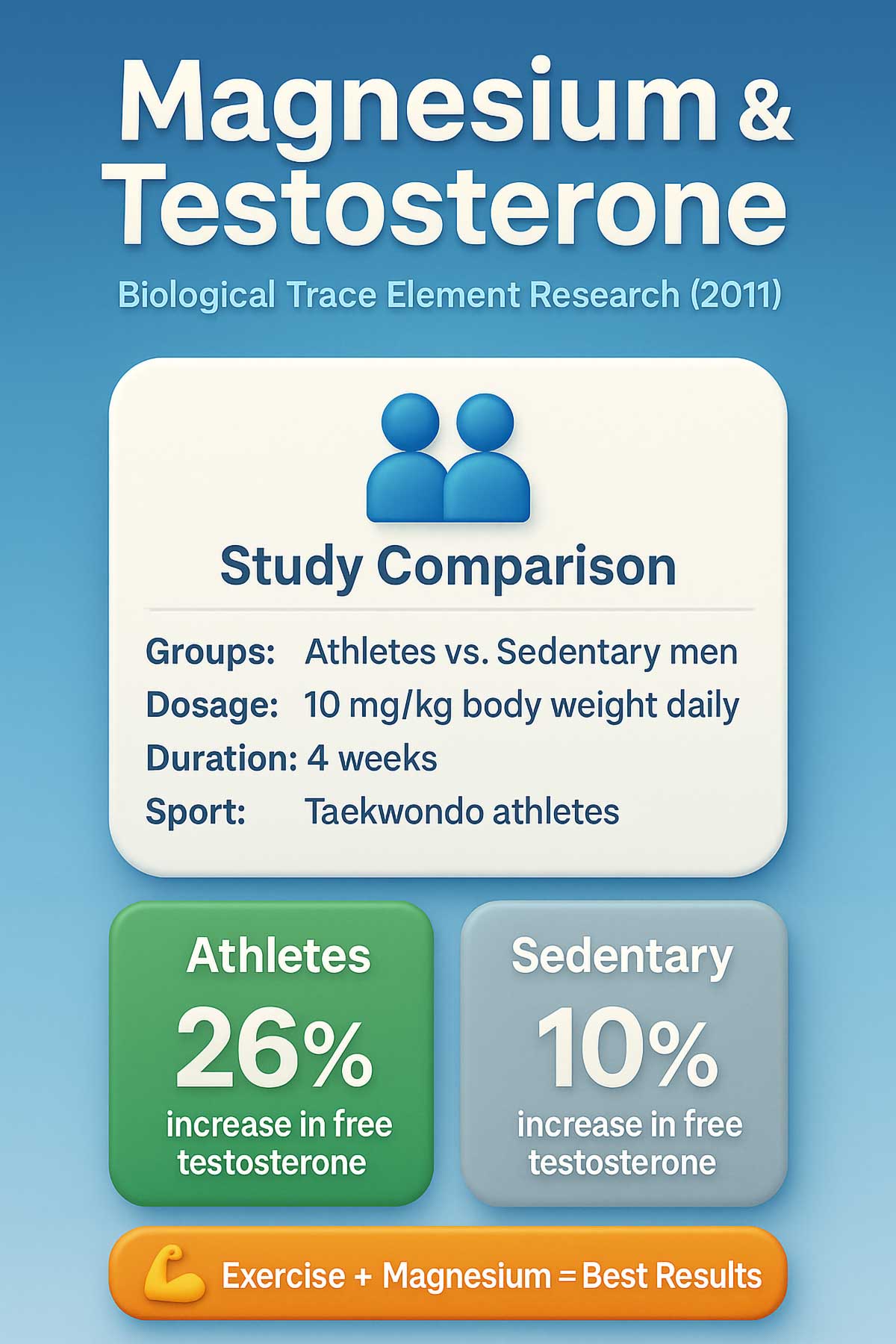
6. Magnesium: The Athlete’s Ally
What Researchers Found: Magnesium supplementation can increase free testosterone, but the effect is significantly stronger in physically active men. Studies show that athletes and regular exercisers benefit most, while sedentary men see minimal changes.
This makes biological sense. Exercise depletes magnesium through sweat and increased metabolic demands. When active men replenish magnesium, their bodies can produce more testosterone. Sedentary individuals don’t have the same depletion issue.
A 2011 study published in Biological Trace Element Research compared sedentary men to taekwondo athletes. Both groups took 10 mg of magnesium per kilogram of body weight daily for four weeks. The athletes showed a 26% increase in free testosterone, while sedentary men saw only a 10% increase. The researchers noted that exercise itself boosted testosterone, and magnesium amplified this effect.
Who It’s Best For: Athletes and men who train regularly. If you’re hitting the gym four or more times per week, magnesium supplementation might support your hormonal health.
The Verdict: ⚖️ Conditional
Like zinc and vitamin D, magnesium only helps when you need it. But unlike those nutrients, the “need” is determined more by activity level than blood tests. Active men burn through magnesium faster and benefit more from supplementation.
How to Take It:
- Dose: 200-400 mg daily. Athletes may need up to 500 mg
- Timing: Take in the evening. Magnesium glycinate taken 30-60 minutes before bed can improve sleep quality
- Form: Magnesium glycinate or citrate absorb well. Avoid magnesium oxide, which absorbs poorly and causes digestive upset
- Cycle: Can be taken continuously
- Interactions: May lower blood pressure slightly. Space apart from calcium supplements by 2+ hours
Part 3: The Underperformer — Fails to Live Up to the Hype
Now let’s talk about the supplement that sounds great in theory but falls flat in practice.
7. D-Aspartic Acid: The Myth Debunked
What Researchers Found: D-aspartic acid looked promising in early animal studies. Rats saw significant testosterone increases, and the supplement industry jumped on the trend. But human trials tell a different story—and it’s not a good one.
Multiple studies in trained men showed no significant increase in testosterone. Zero. The mechanisms that work in rats simply don’t translate to human physiology. Yet marketing materials still cite those outdated animal studies.
A comprehensive 2017 study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition followed resistance-trained men for 12 weeks. Half received 3 grams of D-aspartic acid daily, half got a placebo. The result? No difference in testosterone, muscle mass, or strength between groups. The researchers concluded that D-aspartic acid offers no benefit for men engaged in resistance training.
The research is particularly damning because it focused on the exact population most likely to use this supplement: men engaged in resistance training. If D-aspartic acid was going to work for anyone, it should have been them.
Who It’s Best For: No one, based on current human evidence.
The Verdict: ❌ No Effect
Save your money. D-aspartic acid is a perfect example of how supplement marketing can run ahead of actual science. The hype was built on animal research that never panned out in humans. This one’s a hard pass.

Supplement Dosage Calculator
Get personalized dosage recommendations based on your body weight and activity level
The Research at a Glance
| Supplement | Number of Studies | Total Participants | Average T Increase | Study Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ashwagandha | 5+ RCTs | 400+ men | 10-15% | High |
| Tongkat Ali | 2 meta-analyses | 1,000+ men | 15-20% (in low-T) | High |
| Fenugreek | 1 meta-analysis | 300+ men | 10-12% | Moderate |
| Zinc | Multiple RCTs | 200+ men | Restores to normal | High (for deficient) |
| Vitamin D | 1 meta-analysis | 2,000+ men | Variable | Moderate |
| Magnesium | 3 RCTs | 150+ men | 10-25% free T | Moderate |
| D-Aspartic Acid | 4 RCTs | 200+ men | No change | High (negative) |
The Foundation: 5 Lifestyle Changes That Beat Any Supplement
Let’s be honest. No supplement can compensate for poor lifestyle choices. These five factors have a bigger impact on your testosterone than any pill ever will.
1. Resistance Training (The Non-Negotiable)
Why it works: Heavy compound lifts trigger acute testosterone spikes and signal long-term production. Your body responds to the stress of lifting by maintaining higher baseline hormone levels.
What to do:
- Focus on big movements: squats, deadlifts, bench press, rows, and overhead press
- Train 2-4 times per week. More isn’t always better
- Use weights that challenge you for 6-12 reps per set
- Avoid marathon training sessions. Sessions longer than 90 minutes can increase cortisol and suppress testosterone
- Rest 48-72 hours between training the same muscle groups
The sweet spot is intense but brief. A well-designed 45-60 minute session beats a two-hour slog every time.
2. Body Composition Over Body Weight
Why it works: Fat tissue contains aromatase, an enzyme that converts testosterone to estrogen. The more body fat you carry, especially around your midsection, the more testosterone gets converted to estrogen.
What to do:
- Men above 20% body fat should prioritize fat loss
- Aim for 10-18% body fat for optimal hormonal health
- Don’t crash diet. Extreme calorie restriction (below 1,500 calories for most men) tanks testosterone production
- Lose weight gradually: 0.5-1% of body weight per week maintains hormonal balance
- Preserve muscle while losing fat through resistance training and adequate protein
Studies show that losing just 10% of body weight can increase testosterone by 50-100 ng/dL in overweight men. That’s more than most supplements can deliver.
3. Sleep Architecture Matters
Why it works: Testosterone production peaks during REM sleep. Men who consistently sleep less than 6 hours per night can experience testosterone drops of 10-15% in just one week.
What to do:
- Aim for 7-9 hours nightly. Quality matters as much as quantity
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends. Your body thrives on routine
- Keep your bedroom cool (65-68°F is optimal for sleep quality)
- Make your room dark. Even small amounts of light can disrupt melatonin and sleep cycles
- Limit screens 1 hour before bed. Blue light suppresses melatonin production
- Consider magnesium glycinate (200-400 mg) 30 minutes before sleep for better quality
One study found that men sleeping 4 hours per night had testosterone levels equivalent to men 10-15 years older. Sleep isn’t optional if you care about hormones.
4. Strategic Stress Management
Why it works: Cortisol and testosterone operate on a seesaw. When cortisol stays elevated (chronic stress), testosterone production gets suppressed. Your body can’t maintain both high cortisol and high testosterone simultaneously.
What to do:
- Practice daily stress reduction: 10 minutes of meditation, deep breathing, or quiet time
- Take regular walks in nature. Studies show 20-minute nature walks significantly lower cortisol
- Set firm boundaries at work. Chronic overwork destroys hormone balance
- Reduce social media time. Constant information and comparison fuel stress responses
- Consider ashwagandha if stress is unavoidable (see Part 1)
- Build recovery into your week. You can’t go hard 24/7
The men with the healthiest testosterone levels aren’t stress-free. They manage stress effectively.
5. Nutrition for Hormone Production
Why it works: Hormones require specific nutrients as building blocks. Testosterone is synthesized from cholesterol, and the process requires zinc, magnesium, vitamin D, and adequate calories.
What to do:
- Eat adequate protein: 0.8-1g per pound of body weight daily
- Don’t fear dietary fat. Aim for 30-35% of calories from healthy sources (olive oil, avocados, nuts, fatty fish)
- Include zinc-rich foods: oysters (the king of zinc), beef, pumpkin seeds, cashews
- Eat magnesium sources: dark leafy greens (spinach, Swiss chard), nuts, whole grains, dark chocolate
- Get vitamin D from fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines) or sensible sun exposure
- Don’t crash diet. Eating below your basal metabolic rate signals famine to your body, which shuts down testosterone production
Interestingly, low-fat diets (below 20% of calories from fat) consistently show lower testosterone levels in studies. Your body needs fat to make hormones.
Sample Daily Protocols for Different Goals
Let’s make this practical. Here are three specific daily routines based on common situations.
Protocol 1: The Stressed Professional
Your situation: High-pressure job, moderate exercise, chronic stress affecting energy and mood.
Morning:
- 300 mg ashwagandha with breakfast
- 15-minute walk outside for vitamin D and stress relief
- High-protein breakfast (eggs, Greek yogurt, or protein smoothie)
Afternoon:
- Brief afternoon walk or stretching session
- Avoid caffeine after 2 PM to protect sleep quality
Evening:
- 30-minute resistance training session (3x per week: Monday, Wednesday, Friday)
- Dinner with healthy fats and vegetables
- 400 mg magnesium glycinate 30 minutes before bed
- 7-8 hours sleep in cool, dark room
- No screens after 9 PM
Why this works: Ashwagandha addresses the root problem (stress) while magnesium supports sleep quality. The training sessions are brief enough to avoid adding more stress.
Protocol 2: The Low-T Athlete
Your situation: Blood work shows low-normal or deficient testosterone. You train hard but aren’t seeing results.
Morning:
- 200 mg tongkat ali with breakfast
- Morning resistance training session (heavy compounds, 4x per week)
- Post-workout meal with protein and carbs
Afternoon:
- 30 mg zinc with lunch
- Adequate calories to support training (don’t diet while trying to boost testosterone)
Evening:
- 400 mg magnesium with dinner
- Recovery walk or light yoga
- 8-9 hours sleep (athletes need more than average)
Why this works: Tongkat ali targets low testosterone directly. Zinc and magnesium replenish what you lose through intense training. Extra sleep supports recovery and hormone production.
Protocol 3: The Deficiency-Correction Protocol
Your situation: Blood tests show deficiencies in vitamin D, zinc, or magnesium. Testosterone is low-normal.
Morning:
- 4,000 IU vitamin D with breakfast (include fat sources like eggs or avocado for absorption)
- 30 mg zinc
Afternoon:
- Whole food focus: oysters once weekly, grass-fed beef 2-3x weekly, leafy greens daily
Evening:
- 400 mg magnesium
- Resistance training 3x per week
- Sunlight exposure: 15-20 minutes daily when possible
Retest after 12 weeks: Check vitamin D, zinc, and testosterone levels. Adjust supplementation based on results.
Why this works: You’re correcting documented deficiencies rather than guessing. Combined with resistance training and whole foods, you’re addressing multiple factors simultaneously.
5 Mistakes That Sabotage Testosterone (And How to Avoid Them)
Even with the right supplements, these common errors can undermine your results.
1. Stacking Too Many Supplements at Once
The problem: Taking everything simultaneously makes it impossible to know what’s working. You’re also spending money on supplements you might not need.
The fix: Start with one supplement for 8-12 weeks. Track your energy, strength, and mood. Get blood work if possible. Then assess whether to continue, adjust dose, or add another supplement. This methodical approach saves money and provides clear feedback.
2. Ignoring Dosage Guidelines
The problem: More isn’t better with hormones. Taking 60 mg of zinc daily won’t boost testosterone faster. It’ll impair your immune function and create mineral imbalances.
The fix: Follow research-backed doses listed in this article. If you’re tempted to take more, get blood work instead. Let data guide your decisions, not desperation.
3. Buying Low-Quality Products
The problem: That $10 ashwagandha bottle on Amazon probably contains minimal active compounds. You’re paying for filler, not results.
The fix: Look for third-party testing seals (NSF, USP, ConsumerLab). Check for standardized extracts with specific percentages listed. Yes, quality supplements cost more. But they actually work, making them cheaper in the long run than buying ineffective products repeatedly.
4. Expecting Overnight Results
The problem: Hormonal changes take time. You won’t feel different after one week.
The fix: Give any supplement at least 8 weeks before judging effectiveness. Keep a simple log of energy levels, workout performance, and mood. Subtle changes add up over weeks. Blood work at 12 weeks provides objective data.
5. Supplementing Without Testing
The problem: You might not need supplements at all. Or you’re taking the wrong ones for your situation.
The fix: Get baseline blood work before starting supplements. Test testosterone (total and free), vitamin D, and consider zinc and magnesium if budget allows. Retest after 12 weeks. This approach costs $100-200 upfront but prevents months of wasted money on ineffective supplementation.
How to Choose Quality Supplements
Not all supplements are created equal. The supplement industry is loosely regulated, which means quality varies wildly. Here’s how to spot the good ones.
Look for Third-Party Testing:
- NSF Certified for Sport (tests for banned substances and verifies label accuracy)
- USP Verified (confirms ingredients match the label and tests for contaminants)
- ConsumerLab Approved (independent testing for quality and potency)
These seals mean an outside lab verified what’s in the bottle. Without third-party testing, you’re trusting the manufacturer to police themselves.
Check for Standardization:
- Ashwagandha: Look for “5% withanolides” or “KSM-66” on the label
- Fenugreek: Should specify “Trigonella extract” with standardized furostanolic saponins
- Tongkat Ali: Look for “100:1” or “200:1” extract ratio
Standardization means consistent levels of active compounds in every dose. Generic “fenugreek powder” might contain 1/10th the active compounds as a standardized extract.
Avoid Proprietary Blends: Labels that list a “proprietary blend” without individual ingredient amounts are hiding something. You can’t verify you’re getting research-backed doses. Reputable companies list exact amounts of each ingredient.
Red Flags to Avoid:
- Claims of “doubling testosterone” or similar exaggerations
- No ingredient amounts listed anywhere on the label
- Suspiciously cheap prices (quality extracts cost more to produce)
- Promises of instant results (“feel the difference in 24 hours”)
- Long lists of ingredients (10+ items in one pill)
- No contact information or website for the manufacturer
A quality supplement will list exactly what’s inside, how much, and provide evidence to support their claims.
When Supplements Aren’t Enough: Red Flags to Watch
Some symptoms suggest a medical issue that supplements can’t fix. If you experience any of these, skip the supplements and see an endocrinologist:
- Testosterone below 300 ng/dL on multiple blood tests (taken at the same time of day)
- Sudden, dramatic changes in energy or mood that don’t match life circumstances
- Loss of body hair, particularly facial and body hair that was previously normal
- Breast tissue development (gynecomastia)
- Testicular pain, shrinkage, or changes in size
- Erectile dysfunction that doesn’t improve with lifestyle changes after 3 months
- Extreme fatigue despite adequate sleep (8+ hours nightly)
- Difficulty building muscle despite consistent training and adequate protein
- Rapid, unexplained weight gain, particularly around the midsection
These symptoms can indicate hypogonadism, thyroid problems, pituitary issues, or other hormonal disorders that require medical treatment. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) might be appropriate for some men with clinically low levels. But that’s a decision to make with a doctor, not on your own.
Your Actionable Strategy for Healthy Testosterone
Let’s bring this all together with what you actually need to know.
The Supplement Scorecard:
- Ashwagandha (✅): Best for stressed or training men seeking modest support. Start here if you’re juggling high stress and regular workouts.
- Tongkat Ali (✅): Best for men with clinically low testosterone. Get blood work first to confirm you need this.
- Fenugreek (✅): Best for moderate T and libido support. Good option if sexual health is a priority alongside energy.
- Zinc (⚖️): Only helps if you’re deficient. Athletes, vegetarians, and older adults are most likely to benefit.
- Vitamin D (⚖️): Only helps if you’re deficient. Get tested or supplement during winter months if you live in northern climates.
- Magnesium (⚖️): Best for active men. If you train hard 4+ times weekly, this supports both testosterone and recovery.
- D-Aspartic Acid (❌): Skip it entirely. Save your money for something that actually works.
Your Step-by-Step Action Plan:
- Get baseline blood work (total testosterone, free testosterone, vitamin D). This costs $100-200 and eliminates guesswork.
- Fix lifestyle factors first (sleep 7-9 hours, start resistance training, manage stress, eat adequate protein and fat). Give this 12 weeks before adding supplements.
- Choose one supplement based on your specific situation:
- High stress + training = Ashwagandha
- Confirmed low testosterone = Tongkat Ali
- Zinc/Vitamin D deficiency = Address that deficiency first
- Active lifestyle = Magnesium
- Take it consistently for 8-12 weeks. No skipping doses. Track your energy, strength, and mood weekly.
- Retest blood work at 12 weeks. Compare results to baseline. Adjust or add supplements based on data.
- Don’t stack everything hoping for better results. Two to three supplements maximum. More creates confusion and wastes money.
The Real Secret to Healthy Testosterone
No supplement—not even the effective ones—can replace the basics. Your testosterone levels aren’t determined by what you swallow in pill form. They’re determined by how you live.
A man who sleeps 8 hours, trains with heavy weights three times weekly, maintains 15% body fat, manages his stress, and eats a nutrient-dense diet will have healthy testosterone. He might not need supplements at all.
A man who sleeps 5 hours, never lifts weights, carries excess body fat, lives in constant stress, and eats processed foods will have low testosterone. No supplement will fix that foundation.
Start with the fundamentals. They’re free, they work for everyone, and they deliver bigger results than any pill.
If you’ve mastered the basics and still struggle with low energy, poor recovery, or confirmed low testosterone on blood work, then supplements make sense. Choose them strategically based on your specific situation. Take them consistently. Track your results objectively.
But always go back to the foundation. Sleep. Training. Body composition. Stress. Nutrition. These five factors control your hormonal health more than anything else.
FAQs
Can women take these testosterone supplements?
Most research focuses on men, and women should be cautious. Women naturally produce much less testosterone than men (about 1/10th the amount). Taking supplements designed to boost testosterone could cause unwanted effects like facial hair growth, voice deepening, acne, and menstrual changes. Women concerned about hormonal health should consult their doctor for female-specific recommendations.
How long do I need to take these supplements?
Most research studies last 8-12 weeks, which gives you a good timeframe for initial results. Many people cycle supplements (8-12 weeks on, 2-4 weeks off) to prevent your body from adapting. Nutrients like zinc, vitamin D, and magnesium might need ongoing supplementation if your diet doesn’t provide enough. The herbs (ashwagandha, tongkat ali, fenugreek) work best when cycled.
Will these supplements show up on drug tests?
The supplements themselves are legal and won’t trigger positive drug tests. They don’t contain actual testosterone or anabolic steroids. They work by supporting your body’s natural testosterone production. That said, athletes subject to strict drug testing should verify any supplement with their sport’s governing body. Some organizations have specific banned substance lists.
Can I take multiple supplements together?
Yes, but start with one at a time to assess individual effects. This helps you understand what’s actually working. Common effective stacks include ashwagandha + magnesium for stressed athletes, or tongkat ali + zinc for men with low-T. Avoid taking more than 3-4 supplements simultaneously. You’ll waste money and won’t know which one is helping.
What about testosterone replacement therapy (TRT)?
TRT involves pharmaceutical testosterone prescribed by a doctor. It’s much more powerful than any supplement and will increase testosterone to normal or high-normal levels. But it comes with side effects: testicular shrinkage, reduced fertility, potential cardiovascular risks, and lifelong dependency. Try lifestyle changes and supplements first. But if your levels are below 300 ng/dL and symptoms persist, TRT might be the right choice. That’s a decision to make with an endocrinologist.
Do testosterone boosters work for building muscle?
The modest increases from these supplements (10-15%) are less impactful for muscle building than proper training and nutrition. Don’t expect dramatic muscle gains from supplements alone. They might provide a small edge, but 90% of your results come from consistent training, adequate protein (0.8-1g per pound), progressive overload, and recovery. Fix those first.
Are there foods that boost testosterone naturally?
No single food dramatically raises testosterone, but nutrient-dense diets support hormonal health. Oysters provide exceptional zinc (six oysters contain your entire daily requirement). Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel deliver vitamin D and omega-3s. Eggs supply cholesterol, which your body uses to manufacture testosterone. Leafy greens offer magnesium. A diet rich in these foods creates the foundation for healthy hormone production.
How do I know if a supplement is working?
Track both subjective and objective measures. Subjectively, notice changes in energy levels, workout performance, recovery time, mood, and libido over 8-12 weeks. Keep a simple log. Objectively, get blood work before starting and 12 weeks after. Compare total testosterone, free testosterone, and any nutrients you’re supplementing. Strength gains in the gym provide another concrete measure.
Can I take these supplements if I’m on medication?
It depends on the medication. Always inform your doctor about any supplements you’re taking. Ashwagandha can affect thyroid medication. Fenugreek may alter blood sugar control in diabetics. Zinc can interfere with certain antibiotics. Magnesium might lower blood pressure. Your doctor can review your medication list and flag potential interactions.
What if I’m vegetarian or vegan?
Plant-based diets often run low in zinc, vitamin D, and certain amino acids that support testosterone production. You’re more likely to benefit from zinc supplementation. Consider vitamin D year-round unless you get significant sun exposure. B12 supplementation is also wise for vegans, as it supports overall hormonal health. Include zinc-rich plant foods like pumpkin seeds, cashews, and chickpeas regularly.
At what age should men worry about testosterone?
Testosterone naturally declines about 1% per year after age 30. That’s normal and not necessarily problematic. Start paying attention if you notice symptoms (fatigue, decreased strength, low libido) that affect your quality of life, regardless of age. Men in their 20s with symptoms should get tested. Men over 40 might consider baseline testing even without symptoms, so you know your normal range.
Can stress alone cause low testosterone?
Absolutely. Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which directly suppresses testosterone production. Studies show men in high-stress jobs or experiencing major life stressors can see testosterone drops of 15-25%. This is why ashwagandha (which reduces cortisol) indirectly boosts testosterone. Managing stress might improve your levels more than any supplement.
“`


